Why Fair and Transparent AI Retail Policy Frameworks Matter

Consumers want to feel safe when they shop with AI-powered retailers, especially given the ethical concerns surrounding data usage. Privacy and trust are very important now. Many shoppers worry about how businesses use their data. The table below shows how serious these worries are:
Source | |
|---|---|
Pew Research Center | 81% |
KPMG | 63% |
Brookings Institution | 49% |
Retailers who care about ethical concerns build better relationships with customers. They earn trust by explaining how AI works. They also make fair choices. Clear talk about data use helps people feel safe. Regular checks for bias help protect everyone.
Key Takeaways
Shoppers care about privacy and trust when using AI stores. Stores should tell customers how they use their data to help them feel safe.
Algorithmic bias can cause some groups to be treated unfairly. Stores need to check their AI often for bias to keep things fair.
Being open is important for customer loyalty. Stores should explain how AI makes choices and how they use and collect data.
Good AI policy frameworks keep both shoppers and stores safe. They help stop legal problems and help people trust stores for a long time.
Checking and updating AI rules often shows stores care about doing the right thing. Stores should always work to make their rules better for new problems.
Ethical Concerns in AI Retail
Privacy Risks and Data Use
AI-powered retail platforms gather lots of personal data. Shoppers give retailers their names, addresses, and payment info. Sometimes, they share biometric data too. Using AI can make privacy risks worse. Companies might use personal data without asking first. This is called unauthorized data use. Biometric data worries happen when stores keep fingerprints or face scans. Covert data collection means companies take information secretly.
Privacy Risk | Description |
|---|---|
Unauthorized data use | Use of personal data without consent or knowledge of the consumer. |
Biometric data concerns | Risks associated with the collection and storage of biometric information. |
Covert data collection | Gathering data without the knowledge of the consumer, often through hidden means. |
Discrimination or unfair treatment resulting from biased AI algorithms. |
Retailers get attacked by hackers more because of AI. About 44% of retailers saw more attacks. Last year, 34% had a data breach. Sometimes, private info leaks out, like ChatGPT showing chat histories. AI models can share customer data by accident, even in health apps.
Tip: Retailers should ask before collecting personal data. Customers feel safer when they know how their data is used.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI systems use data to make choices. If the data is biased, results can be unfair. Algorithmic bias changes who gets deals or sees products first. It can even affect prices. An MIT study found facial recognition in stores matched lighter skin 0.8% wrong, but darker skin 34.7% wrong. This shows bias against some groups.
Algorithms can copy and increase human biases, especially for protected groups.
Automated risk checks in U.S. courts gave longer sentences to people of color.
Retailers need to fix fairness problems. Biased data can make wrong predictions and repeat stereotypes. Dynamic pricing can treat people unfairly based on income. AI hiring tools can repeat old discrimination if trained on biased data.
Impact Type | Description |
|---|---|
Disproportionate Representation | AI systems may favor certain demographic groups, leading to skewed recommendations that disadvantage minorities. |
Unintended Discrimination | Subtle biases can result in exclusionary recommendations, ignoring preferences of underrepresented groups. |
Inaccurate Predictions | Models trained on biased data may fail to predict behaviors of historically underserved customers, missing business opportunities. |
Bias in Data Collection | Data sourced from specific regions or demographics can lead to biased generalizations, failing to capture broader market behavior. |
Reinforcement of Stereotypes | Overrepresentation of certain demographics in training data can limit exposure to diverse product offerings, reinforcing stereotypes. |
Discriminatory Pricing Structures | Dynamic pricing algorithms may unintentionally discriminate based on socio-economic status, leading to unfair pricing. |
Replication of Historical Biases | AI hiring tools can replicate past discriminatory patterns if trained on biased historical data. |
Cultural Insensitivity | AI systems trained on non-inclusive datasets may alienate users from diverse backgrounds, impacting customer experience. |
Transparency Challenges
Retailers find it hard to make AI easy to understand. Customers and workers should know how AI affects them. Stores must explain how AI works and why it makes choices. Many companies struggle to mix AI with old systems. They also have trouble finding skilled AI workers. Privacy and bias worries make transparency more important.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Integrating AI solutions with legacy systems can be complex and expensive. | |
Talent Gap | Retailers may face a talent gap in finding qualified AI professionals. |
Ethical Considerations | Ethical concerns about privacy and bias arise when using AI for personalization. |
Cost of Implementation | Significant investment in hardware, software, and personnel is required. |
Explainability and Trust | Lack of understanding of AI decision-making can lead to distrust. |
Change Management | Significant changes to existing processes and workflows are often necessary. |
AI bias can cause unfair suggestions or prices.
Being clear about AI recommendations helps keep customer trust.
Customers want to know when AI is used. They expect stores to explain how their data is used. More transparency makes shoppers feel confident and loyal. If stores are not clear, people get worried and unsure. Many shoppers fear privacy problems and data misuse, which changes what they buy.
Note: Retailers should share a transparency statement and get ready for new rules that protect customer privacy.
Key Principles for Responsible AI
Fairness and Accountability
Responsible AI in retail means being fair to everyone. Retailers must treat all shoppers the same way. They use frameworks to check for bias in AI. These frameworks help stop unfair results. They also protect shoppers’ rights. The table below lists important fairness and accountability standards:
Framework/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
Demographic Parity | Makes sure different groups get similar results from AI. |
Equal Opportunity | Gives equal chances to people with the same skills. |
Predictive Parity | Makes AI predictions just as accurate for all groups. |
Causal Fairness | Treats things like income or education the same for everyone. |
Counterfactual Fairness | Keeps results the same even if someone’s background changes. |
Disparate Impact | Stops unfair benefits for any group, even if sensitive data is not used. |
Audits & Certifications | Requires records and outside checks to follow ethical rules. |
Red Teaming | Uses special tests to find weak spots in AI models. |
Algorithmic & Human Rights Impact Assessments | Checks how AI affects society and basic rights. |
Singapore’s FEAT Principles | Gives rules for using AI in financial services. |
Australian AI Ethics Framework | Shares guidelines for using AI responsibly. |
UNESCO Recommendation on the Ethics of AI | Focuses on ethics during the whole AI process. |
OECD Principles on AI | Gives a common set of rules for AI use. |
Retailers check accountability by watching how AI changes sales and customer actions. They use numbers like sales lift, lead conversion, and basket size. These tools help see if AI is fair and meets goals.
Treat AI like a product with clear goals.
Track profit and loss for each campaign.
Use forecasts before starting new projects.
Keep checking results to see what works.
Use good money habits to help projects succeed.
When stores follow these rules, they fix ethical problems and earn trust.
Tip: Regular checks and clear records show shoppers that stores care about fairness.
Privacy and Security
Privacy and security keep shoppers safe. Retailers should only collect the data they need. They must ask before sharing data with AI tools. Shoppers should be able to see, fix, or delete their data. Automated tools help keep information safe. Privacy Impact Assessments find risks and help fix them early.
Use tools to map data and check vendor risks.
Do Privacy Impact Assessments to spot and fix problems.
Set up consent tools to track permissions.
AI privacy tools help stores follow rules like GDPR. These tools handle data safely and build trust. Protecting privacy helps avoid big problems and keeps a good reputation. The table below shows how privacy and security issues can hurt stores:
Statistic | Impact |
|---|---|
82% of consumers | Left a brand because of data worries |
48% of consumers | Stopped buying from stores over privacy fears |
33% of consumers | Cut ties with brands due to privacy problems |
Average cost of a data breach | $4.45 million each time |
One data breach can cause bad news and lost shoppers. Losing trust is a big problem, and many people leave brands over privacy.
Note: Protecting privacy is not just about rules. It is about earning trust and keeping business strong.
Transparency in Practice
Transparency means stores explain how AI works and uses data. Shoppers want to know why they see certain products or prices. Stores must show how AI makes choices. They should talk clearly with shoppers and answer questions about AI.
Write down how AI makes decisions.
Tell everyone how data is used.
Talk openly with shoppers about AI.
Stores can be transparent by showing how they make recommendations. They should explain their choices in simple words. Feedback from workers helps make AI better and fairer. Easy-to-use tools turn data into ideas shoppers can understand.
Show how recommendations are made.
Explain choices in simple words.
Use worker feedback to improve AI.
Make tools that turn data into easy tips.
Clear talk helps people understand AI. This helps stores fix ethical problems and build trust.
Tip: Sharing transparency statements and talking openly makes shoppers feel safe and loyal.
Real-World Impact

Poor Frameworks: Consequences
Weak AI retail policy frameworks can cause big problems for stores and shoppers. If companies do not have clear rules for data, they might break privacy laws. This can mean large fines and lost trust. For example, a healthcare group in Europe paid $250,000 for using an AI transcription tool that broke GDPR. Apple Card’s AI gave women lower credit limits than men with the same money. This bias made people angry and hurt Apple’s name.
Bad data handling and no consent can break privacy rules.
Secret data use makes customers lose trust and hurts business.
Companies can get fined and get bad news after privacy leaks, like with Cambridge Analytica.
Algorithmic bias can cause unfair treatment and legal problems.
When shoppers stop trusting a brand, they often stop buying. Businesses then have a hard time fixing their name and sales.
Strong Frameworks: Benefits
Retailers with strong AI policy frameworks get real benefits. They earn trust by keeping data safe and making fair choices. Visual Comfort & Co. used Microsoft Dynamics 365 to link data in 56 showrooms. This gave them real-time inventory, cut processing time by 28%, and made orders more accurate. Customers saw better service and faster orders.
Starbucks used AI in its rewards program and got 15% more active members. Loyalty members now make up 41% of U.S. sales.
Almost 70% of brands see more customer engagement from loyalty programs.
58% of brands get more repeat buyers with strong AI tools.
AI helps stores give personal shopping, which grows loyalty and sales.
Retailers with clear, fair AI policies get loyal customers and better sales. Shoppers feel safe and important, so they keep coming back.
Best Practices for Retailers and Consumers
Safeguards for Ethical AI
Retailers can set a good example by using clear safeguards. They need to manage data carefully and always ask before collecting it. Regular checks help find and fix bias in AI models. Strong privacy tools, like encryption, keep data safe. Retailers must tell people how AI makes choices and set rules for responsibility. They should update their ethical rules often to handle new risks.
Be open about collecting data and getting consent.
Use different kinds of data and check for bias often.
Keep data private with strong security and anonymization.
Explain AI choices in simple ways to shoppers.
Keep improving ethical rules as things change.
A new survey found 88% of people want brands to make rules for ethical AI. About 86% think brands should watch for AI bias, and 83% want brands to talk openly about using AI.
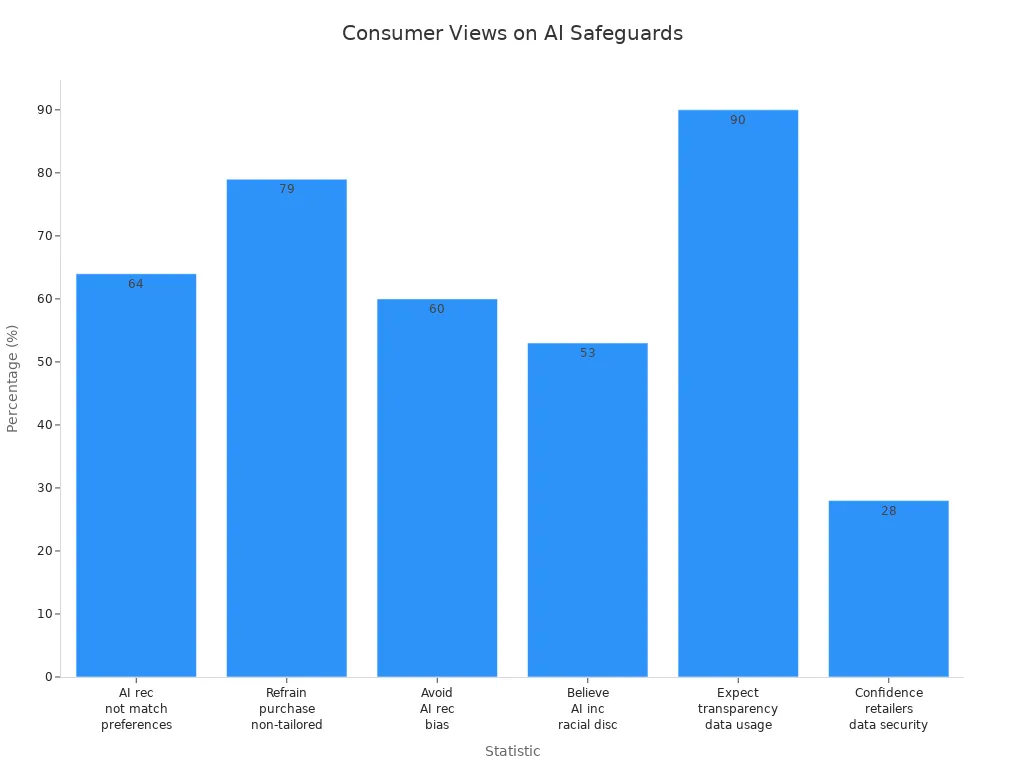
Consumer Protection Steps
Consumers can do things to keep their privacy and rights safe. They should read privacy statements and ask how stores use their data. Most shoppers want stores to be clear, with 90% wanting to know how their data is used. People can use privacy settings and say no to sharing data when they can. In Canada, laws let shoppers cancel online sales and subscriptions. In the Middle East, people care more about data safety and green choices. These steps help shoppers stay safe and know what is happening.
Tip: Consumers should look for clear privacy rules and use their rights to control their own data.
Regulatory Compliance
Retailers must follow strict rules to stay out of trouble and build trust. Important ideas are safety, fairness, openness, and responsibility. Companies should let users question AI choices and get help if needed.
Description | |
|---|---|
Safety, security & robustness | Keep AI systems safe and secure. |
Transparency & explainability | Clearly explain how AI works. |
Fairness | Prevent bias and ensure fair outcomes. |
Accountability & governance | Set clear roles for oversight. |
Contestability & redress | Allow users to challenge decisions and seek redress. |
Retailers should teach workers, watch how AI is used, and update rules to follow new laws. These steps help fix ethical problems and keep everyone safe.
Building Trust Through Policy

Clear Communication
Retailers need to talk clearly about how they use AI. Customers want to know how their data is collected and used. When companies share this, shoppers feel safer and more sure. Only 22% of people trust stores to use their data right. This number gets even lower when generative AI is used. Brands that let customers help with AI rules show respect. These brands become partners, not just sellers.
Being open about AI and data use helps build trust.
People want to know what happens to their information.
71% of shoppers in the U.S. will pay more to brands they trust with their data.
Stores should use easy words and answer questions clearly. They can give updates by email, on websites, or with signs in stores. When shoppers understand AI, they feel more in control. This makes them want to come back and shop again.
Tip: Brands should ask for feedback and listen to what customers say about AI. This helps everyone work together.
Ongoing Accountability
Accountability helps keep trust strong over time. Stores must set clear rules for how AI works and who checks it. People need to watch over AI to make sure it is fair. Companies keep track of every AI choice, so mistakes are easy to find and fix. An AI Steering Committee can help make rules, approve changes, and handle problems.
Checking and reviewing AI often keeps things honest.
Clear rules help everyone know what to expect.
People watching over AI builds trust and stops problems.
Good stores know strong customer bonds help them grow. They try to meet needs and talk to shoppers at the right time. 78% of people care about sustainability, and 73% will pay more for brands that help the planet. Keeping up with accountability shows a brand cares about ethics and loyalty.
Note: Stores that stay open and responsible build trust that lasts with their customers.
Fair and transparent AI retail policy frameworks help stores act ethically. They make shopping better for people and the planet. These rules help everyone trust stores for a long time. They also make partners and workers feel more confident. Clear rules show who is responsible for AI decisions. Companies that use these frameworks become leaders in their field. The European Union’s AI Act is an example of how rules can help. It shows how being open and responsible can shape new laws. Both stores and shoppers should care about privacy, fairness, and trust. Good policies make everyone feel safe and valued.
Help customers and partners trust stores for a long time
Make partners and workers feel sure about AI tools
Show who is responsible for what AI does
FAQ
What is an AI retail policy framework?
An AI retail policy framework gives rules for how stores use AI. It helps protect customer privacy, stop bias, and build trust. Stores use these rules to make fair choices and keep shoppers safe.
How does a fair AI policy help customers?
Fair AI policies protect shoppers from unfair treatment. They make sure stores use data safely and explain how AI works. Customers feel safer and trust stores more.
Why should retailers focus on transparency?
Transparency builds trust. When stores share how they use AI and data, shoppers feel confident. Clear talk helps customers understand their rights and make smart choices.
What can shoppers do to protect their data?
Shoppers can read privacy statements, use privacy settings, and ask questions. They should look for stores that explain how they use data. Taking these steps keeps personal information safe.
Are there laws for AI in retail?
Many countries have laws for AI and data use. The European Union’s AI Act sets strong rules. Retailers must follow these laws to avoid fines and keep customer trust.
See Also
The Future of Retail Lies in AI-Driven Stores
Understanding the Growth of AI-Enhanced Corner Shops
Transforming Online Retail Management with AI Tools
