Japan's Vending Machine Culture

Japan's vending machine culture stands out in urban landscapes, where one vending machine serves every 23 people—an unmatched global ratio.
With over 5.5 million machines across the country, these automated kiosks appear everywhere: train stations, busy streets, and even temple grounds.
The sheer variety impresses: drinks, fresh food, electronics, and cosmetics all find a place behind glass panels. Japan's vending machine culture thrives due to reliability, convenience, and seamless integration into daily routines.
Statistic Description | Value / Detail |
|---|---|
Vending machine to person ratio | |
Total number of vending machines | Over 5.5 million |
Urbanization rate | Approximately 91.9% |
Product range | Drinks, food, electronics, cosmetics, more |
Key Takeaways
Japan has the highest density of vending machines worldwide, with one machine for every 23 people, offering drinks, food, electronics, and more.
Vending machines operate 24/7, providing reliable, quick, and self-service access that fits into daily life and reflects Japanese values of trust, politeness, and cleanliness.
Advanced technology like AI, cashless payments, and remote monitoring keeps machines efficient, secure, and user-friendly for all ages.
Vending machines support local communities by addressing labor shortages, offering regional products, and providing essential goods even in remote areas.
Sustainability efforts include energy-saving designs, solar power, and recycling initiatives, showing Japan’s commitment to eco-friendly vending solutions.
Vending Machine Culture
Ubiquity in Japan
Japanese vending machines appear everywhere, from bustling city corners to quiet countryside roads. The country leads the world in vending machine density, with one machine for every 23 people. This high concentration means that people rarely walk more than a few steps without seeing a machine. The machines line train platforms, shopping arcades, office buildings, and even remote mountain paths. Their outdoor presence remains unmatched, operating reliably in all weather conditions.
The following table highlights the impressive scale and growth of vending machines in Japan:
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Number of vending machines | |
Population | Approximately 125.7 million |
Density (machines per people) | 1 machine per 23 people |
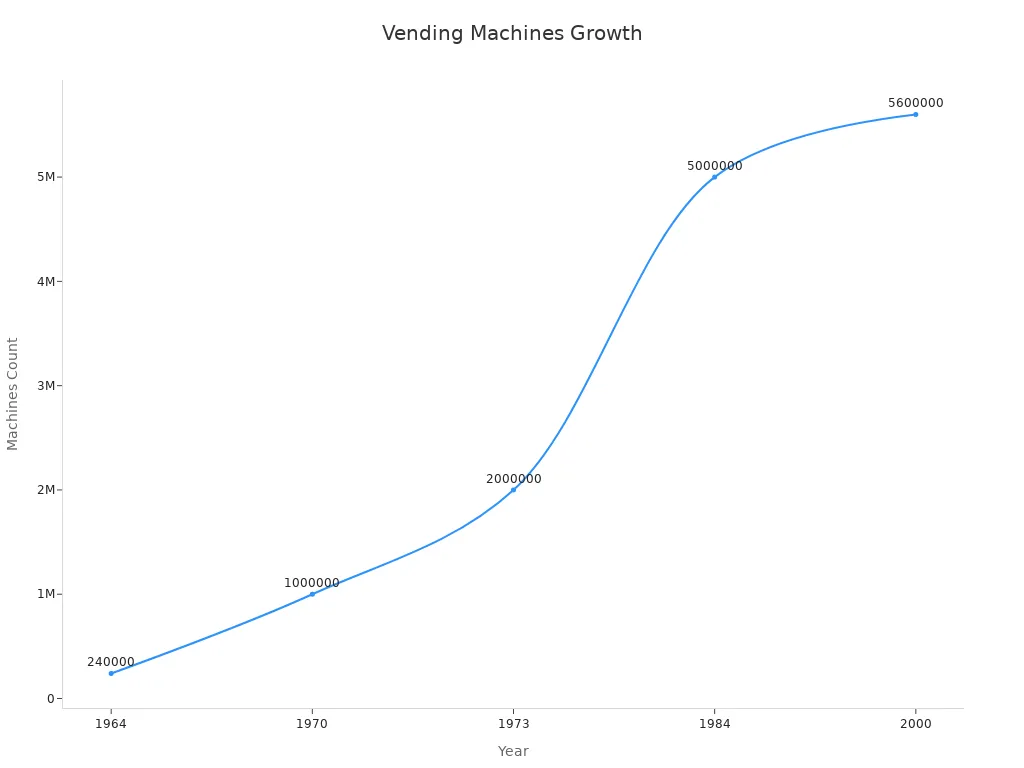
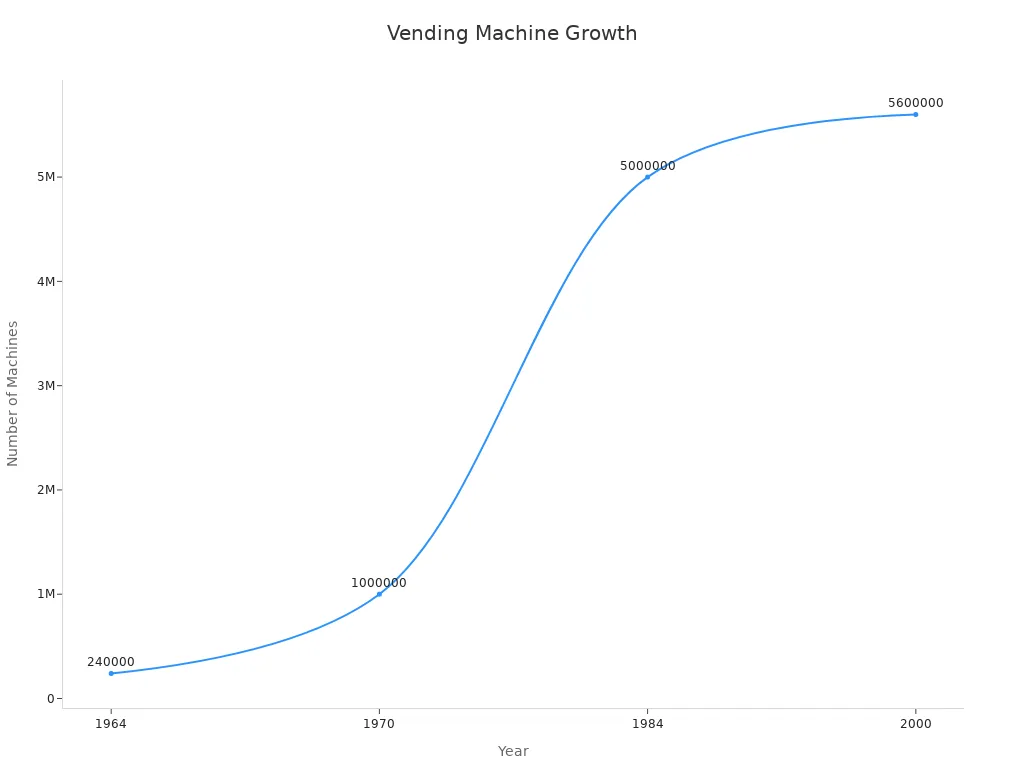
Historical growth milestones | 1964: 240,000 machines |
1970: 1 million machines | |
1973: 2 million machines | |
1984: 5 million machines | |
2000: 5.6 million machines |
Japan's vending machine culture thrives on accessibility. Machines offer self-service options for drinks, snacks, and daily necessities at any hour. People rely on these machines for quick refreshment or a meal, especially when stores close. The sheer number of machines demonstrates how deeply self-service has become part of daily life.
Social Values Reflected
Japanese vending machines do more than sell products. They mirror important social values. Punctuality stands out as a core principle. Machines operate 24/7, never closing or running late. People trust that a cold drink or hot coffee will always be available, even in the early morning or late at night.
Politeness also shapes the vending machine experience. Machines greet users with friendly messages and clear instructions. Many models thank customers after each purchase. This attention to manners reflects the broader culture of respect in Japan.
Self-service defines the interaction with these machines. People expect to complete transactions quickly and independently. The process requires no staff, reducing wait times and encouraging efficiency. Self-service also supports privacy, allowing users to buy what they need without conversation or judgment.
Japan's vending machine culture highlights the nation's commitment to order and cleanliness. Machines rarely show signs of vandalism or neglect. Streets remain tidy, and machines function smoothly. This environment encourages people to respect public property and maintain shared spaces.
The cultural significance of Japanese vending machines extends beyond convenience. These machines represent a blend of technology, trust, and tradition. They show how self-service can support a harmonious society, where people value both independence and community.
History of Japanese Vending Machines
Early Innovations
Japanese vending machines have a long and fascinating history. The first vending machine in Japan appeared in 1888. Takashichi Tawaraya invented a machine that sold postage stamps and postcards. This early device marked the beginning of automated retail in the country. By the 1920s, confectionary vending machines started to gain popularity. These machines offered sweets and small snacks, making them popular among children and busy workers.
The following table shows key moments in the early development of japanese vending machines:
Year | Number of Vending Machines in Japan |
|---|---|
1888 | First vending machine invented by Takashichi Tawaraya |
1920s | Confectionary vending machines begin to gain popularity |
1964 | 240,000 machines |
1970 | 1,000,000 machines |
1973 | Over 2,000,000 machines |
1984 | 5,000,000 machines |
2000 | 5,600,000 machines |
Note: The steady increase in machine numbers shows how quickly the technology spread across Japan.
Growth Since the 1950s
The real expansion of japanese vending machines began in the late 1950s. In 1956, the "Fountain-style Juice Dispenser" arrived, offering fresh juice at the push of a button. This innovation changed how people bought drinks. By 1964, Japan had 240,000 vending machines. The number soared to one million by 1970 and reached five million by 1984.
Japanese vending machines became more advanced over time. Companies introduced machines that could serve both hot and cold drinks. Some models even offered full meals. The rapid growth reflected Japan’s focus on convenience, technology, and customer satisfaction. Today, these machines stand as symbols of innovation and efficiency in everyday life.
Japanese Vending Machines: Products

Drinks and Snacks
Japanese vending machines deliver a wide array of vending machine drinks and snacks to people across the country. These machines offer more than just soda or water. They provide carbonated beverages, still water, and even unique options like oxygen cocktails. Coffee remains a staple, with both hot and cold varieties available year-round. Green tea, a favorite in Japan, appears in many machines, often alongside seasonal flavors.
The selection of snacks continues to grow. People can find ready-made sandwiches, rice balls, and sweet treats. Some machines cater to health-conscious consumers by offering yogurts, curds, and fresh fruits. Schools and offices benefit from these healthy-eating options, making nutritious choices more accessible.
Note: Japan introduced the world's first hydrogen-powered vending machine, showing a commitment to innovation and sustainability.
The table below highlights common vending machine offerings:
Category | Examples |
|---|---|
Drinks | Coffee, green tea, soda, water, oxygen cocktails |
Snacks | Sandwiches, rice balls, chips, sweets |
Healthy Options | Yogurt, curds, fruits |
People enjoy the convenience and reliability of these machines. The wide array of vending machine drinks ensures that everyone can find something to suit their taste.
Vending Machine Food in Japan
Vending machine food in Japan stands out for its quality and variety. Many machines serve hot meals, such as ramen, udon, and curry rice. These meals come freshly prepared and ready to eat. Office workers often rely on lunchomats, which provide quick, satisfying options during busy days.
Some interesting vending machines offer regional specialties. For example, travelers may find machines selling local sweets or unique snacks only available in certain areas. This approach allows people to experience new flavors without visiting a restaurant.
Vending machine food in Japan also includes non-food items. Hygiene products, flowers, and even small electronics appear in some machines. This diversity reflects the changing needs of modern consumers.
Tip: Many machines display clear instructions and polite messages, making the experience easy for everyone, including tourists.
The variety and accessibility of vending machine offerings make them an essential part of daily life in Japan.
Gachapon and Unique Items
Gachapon machines, also known as capsule toy dispensers, have become a cultural phenomenon in Japan. These machines attract collectors and casual shoppers alike. People enjoy the thrill of receiving a random toy or limited-edition item. The collectible nature of gachapon toys drives repeat purchases and strong demand.
Several factors contribute to the popularity of gachapon and other unique items:
Collaborations with popular anime, manga, and gaming franchises boost appeal.
Limited-edition and rare items attract collectors.
Placement in high-traffic areas, such as malls and amusement parks, increases visibility.
Integration of technology, like cashless payments and mobile apps, enhances the user experience.
Social media and online platforms expand access to exclusive items.
Japan's strong culture of collecting and established manufacturing capabilities support its leadership in the gachapon market. Major companies like Bandai and Tomy continue to innovate, offering premium lines and themed releases. Themed entertainment zones and special events often feature exclusive gachapon items, drawing crowds and increasing excitement.
The fascination with interesting vending machines and unique products shows no sign of slowing down. As technology advances, vending machine offerings will likely become even more diverse and engaging.
Technology and Design

Smart Features
Japanese vending machines lead the world in smart technology. Many machines use AI-powered inventory management, facial recognition for personalized offers, and biometric authentication for secure transactions. These features help operators track sales and restock products efficiently. Touchscreen interfaces make the buying process simple and interactive for users of all ages. Remote monitoring allows companies to fix problems quickly and keep machines running smoothly.
Feature Category | Details |
|---|---|
AI Technologies | Facial recognition, AI inventory, biometric authentication |
Security Features | Theft prevention, advanced AI security |
Data Analytics | AI and IoT for consumer data, product placement, marketing optimization |
User Statistics | High demand for 24/7 access, contactless transactions |
Leading Companies | Fuji Electric, Sanden Vendo |
Automated retail in Japan continues to grow as urbanization and smart city initiatives drive demand for convenience and efficiency. The Asia-Pacific region, including Japan, shows the fastest growth and highest concentration of these advanced machines.
Payment Systems
Payment systems in Japanese vending machines have changed rapidly. Cashless and contactless payment methods now dominate the market. Recent research shows that 71% of all vending machine transactions in Japan use cashless payment systems. This marks a 17% increase from the previous year, showing a strong shift away from cash. Users can pay with IC cards, mobile wallets, or QR codes, making purchases quick and easy. Automated retail benefits from these systems by reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Technology Integration | Details |
|---|---|
Cashless Payment Systems | IC cards, mobile payments, QR codes |
Touchscreen Interfaces | User-friendly, supports multiple languages |
Remote Monitoring | Real-time status updates, maintenance alerts |
Automated retail now serves a wide range of users, including children, working professionals, seniors, and tourists. The focus on digital transformation and sustainability continues to drive innovation in payment technology.
Creative Designs
Japanese vending machines stand out for their creative and thoughtful designs. Many machines display polite messages and offer clear instructions, making the experience pleasant for everyone. Some interesting vending machines feature photobooths, refrigeration, or even augmented reality, turning a simple purchase into a fun and memorable event.
Creative design elements, such as user-friendly layouts and quirky features, make transactions quick and enjoyable. These features align with Tokyo’s culture of efficiency and creativity, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Modern automated retail machines often use bright colors, themed exteriors, and playful branding to attract attention. Companies like Fuji Electric and Sanden Vendo continue to innovate, ensuring that vending machines remain both functional and delightful. As a result, customer engagement and brand loyalty increase, making vending machines a unique part of Japan’s urban landscape.
Experiencing Japan's Vending Machines
Everyday Convenience
Experiencing japan's vending machines means seeing self-service in action at every turn. These machines appear on city streets, train stations, parks, and even rural areas. People rely on them for quick access to drinks, snacks, and even hot meals like ramen or gyoza. The machines operate 24/7, so anyone can buy what they need at any hour. Self-service allows users to make purchases without waiting in line or interacting with staff.
Cashless payment systems let people pay quickly, supporting round-the-clock use.
AI-driven inventory control and IoT monitoring keep machines stocked and working.
Touchscreens provide product information and multilingual support.
Universal design features, such as low buttons and handrails, make self-service accessible for everyone, including children and seniors.
Machines offer products tailored to local needs, like hydration drinks during hot summers.
Self-service vending machines act as mini convenience stores, always ready to serve. Office workers, students, and travelers all benefit from this reliable access. The integration of self-service into daily routines shows how much Japan values efficiency and accessibility.
Safety and Trust
Safety and trust play a major role in the success of self-service vending machines. People trust that machines will work properly and provide quality products. The machines rarely show signs of vandalism or neglect, which encourages more people to use them. Self-service reduces the need for staff, lowering costs and making shopping more affordable.
Machines operate in both busy and remote locations, showing the high level of public trust.
Automated systems ensure that products stay fresh and safe.
Self-service supports privacy, letting users buy items without judgment.
Many machines display polite messages, reinforcing a culture of respect.
Experiencing japan's vending machines means enjoying a safe, clean, and reliable self-service environment. The combination of trust, safety, and low-cost shopping makes these machines a vital part of Japanese daily life.
Economic and Social Impact
Market Size
Japan leads the world in the vending machine industry. Over 5 million machines operate across the country, offering everything from drinks to electronics. Data Bridge Market Research identifies Japan as a global leader, highlighting the advanced vending solutions found throughout the nation. The vending machine industry generates significant revenue. Statista projects that the industry will reach approximately 1.0 billion U.S. Dollars by 2024. This figure demonstrates the strong economic impact of vending machines in Japan. Companies continue to invest in new technology and product diversity, ensuring the vending machine industry remains a vital part of the national economy.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Number of vending machines | Over 5 million |
Projected 2024 revenue | 1.0 billion U.S. Dollars |
Global leadership | Advanced vending solutions |
The vending machine industry supports manufacturers, suppliers, and service providers. Many small businesses benefit from machine placement and maintenance contracts. The industry’s scale ensures stable jobs and steady growth for related sectors.
Community Role
The vending machine industry plays a key role in supporting local communities. In Japan, machines act as labor multipliers, especially in an aging society. They perform tasks that would otherwise require human workers, helping address labor shortages. This automation frees up people for other productive work. The vending machine industry also provides 24/7 access to essential goods, which supports daily life in both urban and rural areas.
Machines offer reliable service during emergencies, such as free drinks from emergency vending machines.
Operators use real-time inventory tracking to keep products fresh and available.
Many machines support cashless payments, making purchases easy for everyone.
The vending machine industry often collaborates with local businesses, offering regional specialties and supporting small entrepreneurs.
Vending machines complement konbini, or convenience stores, by filling gaps in service and reaching locations where stores may not operate. The vending machine industry helps build community resilience and ensures that people have access to goods at all times.
Sustainability and Future Trends
Green Initiatives
Japanese vending machines continue to evolve with a focus on sustainability. Manufacturers design machines to use less energy and reduce their environmental impact. Many new models feature LED lighting and energy-efficient cooling systems. Some machines even use solar panels to generate power, helping to lower carbon emissions.
Recycling also plays a role in Japan’s vending machine culture. Many machines stand next to recycling bins, making it easy for people to dispose of bottles and cans responsibly. Companies encourage users to recycle by providing clear instructions and visible reminders.
A nationwide experiment in Japan tested the effect of providing verbal information about eco-friendly coffee in over 10,000 coffee vending machines. Sales of eco-friendly coffee increased by 7% in social spaces like office buildings. This result suggests that people feel motivated to make greener choices when they know their actions help build a positive reputation in their community.
While technical advances in recycling and energy efficiency continue, consumer behavior also shapes the green movement. Information and education can drive real change, showing that sustainability is not just about technology but also about people’s choices.
Next-Gen Machines
Japan’s vending machines lead the way in adopting advanced technology. Companies integrate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and biometric sensors to analyze consumer behavior and automate restocking. IoT connectivity allows real-time inventory tracking and predictive maintenance, keeping machines stocked and running smoothly.
Cashless payment systems, including QR codes and mobile wallets, make purchases fast and hygienic.
Touchscreen controls and intelligent customer service features improve the user experience.
Smart vending machines offer personalized recommendations and let users customize drinks by temperature or ingredients.
The market for vending machines in Japan is growing quickly. Experts project it will reach over USD 1 billion by 2030. Urbanization, smart city initiatives, and changing lifestyles drive this growth. Companies also focus on sustainability, using eco-friendly refrigerants and recyclable materials. Next-generation machines will continue to blend convenience, technology, and environmental responsibility, shaping the future of automated retail in Japan.
Tips for Tourists
Using Japanese Vending Machines
Tourists in Japan encounter vending machines almost everywhere. These machines appear in train stations, parks, shopping districts, and busy city streets. Over 1 million vending machine uses occur annually in major cities, with tourists making up about 60% of all users. Kyoto, Tokyo, and Osaka see the highest activity, especially on weekends and during spring and summer. Self-service vending machines help travelers stay refreshed and reduce urban congestion.
Statistic Category | Details |
|---|---|
Annual Usage | Over 1 million uses annually in major cities |
Tourist Usage Percentage | Tourists account for approximately 60% of all rentals |
Peak Usage Times | Weekends, holidays, spring and summer months |
Popular Locations | Kyoto, Tokyo, Osaka, parks, shopping districts, train stations |
Impact | Enhances tourist mobility and experience; reduces urban congestion |
To use a self-service vending machine, insert coins or bills first. Most machines accept 1,000 yen bills, 500 yen, 100 yen, and 10 yen coins. Digital machines allow IC card payments. After payment, press the button under your chosen item. Collect your drink or snack and remember to take your change from the tray.
Tip: Look for machines with English instructions or use a translation app for help.
Must-Try Items
Japan’s self-service vending machines offer more than just water or soda. Many travelers enjoy trying canned coffee, green tea, and seasonal drinks. Hot drinks become popular in winter, while cold beverages refresh during summer. Some machines sell unique snacks, such as rice balls, sandwiches, or even local sweets. Gachapon machines dispense capsule toys, which make fun souvenirs. In some areas, self-service machines provide hot meals like ramen or curry rice.
Popular vending machine items for tourists include:
Canned coffee (hot or cold)
Green tea
Regional soft drinks
Gachapon capsule toys
Hot meals (ramen, curry rice)
Local specialty snacks
Exploring these self-service options adds excitement to any trip.
Etiquette
Proper etiquette ensures a smooth self-service experience. Insert payment before making a selection. Machines accept specific coins and bills, but not 1 or 5 yen coins. For digital machines, tap your IC card before choosing. Select your item by pressing the button below it. Hot drinks require caution, as they can be very warm. If an item is sold out, a flashing red light or no response will indicate this. Always collect your change from the tray.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Payment Method | Insert payment first (1,000 yen bills, 500 yen, 100 yen, 10 yen coins accepted; 1 and 5 yen coins not accepted). Digital touch-pad machines accept IC cards tapped before selection. |
Selection Process | After payment, select beverage by pushing button underneath. Machines offer hot (seasonal) and cold drinks. Labels may be in Japanese, making selection difficult for first-time users. |
Handling Change | Collect change from the tray after purchase; coins make noise when dispensed to remind users. |
Etiquette Advice | Insert payment first, be careful with hot drinks, be mindful of sold-out items (indicated by flashing red or no reaction). |
Language Barrier | Many machines lack English explanations, which can confuse first-time users. |
Note: Many self-service machines do not have English labels. A translation app or asking a local for help can make the process easier.
Japan’s vending machine culture stands as a symbol of innovation and daily convenience. Machines appear everywhere, offering everything from hot meals to unique products. The following table highlights key aspects:
Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
Density | |
Market Value | |
Technology | IoT, AI, cashless payments, multilingual support |
Social Impact | Supports aging society, promotes sustainability, adapts to new trends |
These machines reflect Japanese values of efficiency, trust, and respect. Visitors can discover this culture firsthand and witness how vending machines continue to evolve and shape modern Japan.
FAQ
What makes Japanese vending machines different from those in other countries?
Japanese vending machines offer a wider range of products, including hot meals, toys, and electronics. They use advanced technology, such as cashless payments and AI features. Machines operate reliably and remain clean, reflecting Japan’s values of efficiency and respect.
Can tourists use Japanese vending machines easily?
Most vending machines accept coins, bills, and IC cards. Many machines display simple instructions. Some offer English menus. Tourists can use translation apps if needed. The process remains straightforward for most visitors.
Are vending machines safe to use at night?
Japanese vending machines operate 24/7 in both busy and quiet areas. Streets remain well-lit and safe. People trust these machines at any hour. Security cameras and regular maintenance help ensure safety.
What are some unique items found in Japanese vending machines?
People can buy fresh flowers, umbrellas, hot meals, and even t-shirts. Gachapon machines dispense collectible toys. Some machines sell regional snacks or limited-edition drinks. The variety surprises many first-time users.
How do vending machines support sustainability in Japan?
Manufacturers design machines with energy-saving features, such as LED lights and solar panels. Many machines stand next to recycling bins. Companies encourage users to recycle bottles and cans. These efforts help reduce environmental impact.
See Also
Discovering Tokyo’s Sake Machines For An Authentic Experience
A Journey Through Tokyo’s Innovative Sake Vending Spots
Automated Machines Offering Exclusive Band Merchandise Items
