How Powered Technology is Transforming Grocery Store Accessibility

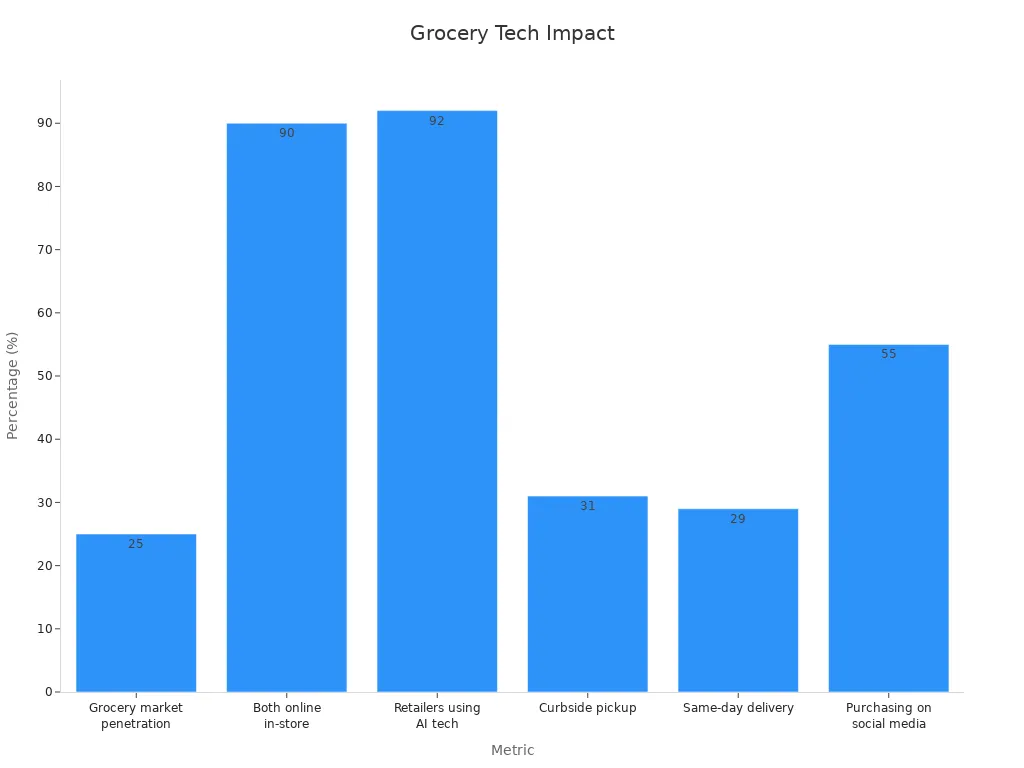
Powered technology changes the grocery shopping experience by making it easier for every customer. Artificial intelligence, smart carts, and contactless payment help customers shop with less stress. Online platforms offer more choices and support for people with special needs. Over 90% of shoppers now use both online and in-store options, showing the impact of technology on accessibility. Many customers spend more online, with the average online grocery order reaching $109 per transaction.
Key Takeaways
Powered technology like AI and smart carts makes grocery shopping easier, faster, and more personalized for all customers.
In-store navigation tools and assistive features help shoppers, especially those with disabilities, find products and move around stores with less stress.
Smart carts and contactless payments reduce physical effort and speed up checkout, improving convenience and accessibility.
Online grocery platforms and real-time inventory tracking offer flexible shopping options and reliable product availability.
Stores must balance innovation with privacy, security, and user-friendly design to ensure technology benefits everyone.
Powered Technology in Grocery Shopping
Personalization with AI
Artificial intelligence changes the way customers shop for groceries. AI studies shopping habits and learns what each customer likes. Stores use this information to create personalized shopping experiences. For example, AI suggests smart product recommendations based on past purchases. These suggestions help customers find new products they might enjoy.
AI-powered algorithms also help stores send personalized promotions. These offers match each customer’s needs and increase satisfaction. Over 92% of online shoppers have interacted with AI customer service. This interaction leads to higher satisfaction and loyalty. AI applications in grocery retail, such as personalized promotions, have increased sales by 4% to 8%. Operating profit has also grown by 2% to 3%. AI uses data from loyalty programs and point-of-sale systems to improve inventory and pricing. This process makes grocery shopping easier and more enjoyable for everyone.
Tip: Customers can use predictive shopping lists created by AI. These lists save time and make shopping more efficient.
The table below shows how leading companies use powered technology and artificial intelligence to improve the grocery shopping experience:
Company | Technology Used | Impact / Measurable Data |
|---|---|---|
AI, Computer Vision, IoT | Cashierless stores eliminating checkout lines, creating seamless shopping experience | |
Walmart | AI, Big Data Analytics, Mobile Apps, AI Robots | Mobile app for online shopping and personalized offers; AI robots for inventory management; real-time stock monitoring |
Tesco | Big Data Analytics, AI | Personalized marketing via Clubcard loyalty program; omnichannel shopping platforms |
Market Data | - | Global grocery delivery market projected to reach US$770.90bn by 2024 with CAGR of 11.81% until 2029 |
Technologies | AI-driven demand forecasting, RFID smart carts, mobile payments, robotics, blockchain | Enhanced inventory management, personalized marketing, supply chain transparency, and improved checkout experience |
AI and data analytics also help stores forecast demand. This process reduces food waste and keeps shelves stocked. Customers benefit from better product availability and more personalized experiences.
In-Store Navigation Tools
In-store navigation tools guide customers through grocery stores. These tools use powered technology to make shopping easier, especially for people who need extra help. Interactive maps and virtual assistants show customers where to find products. For example, Mapsted’s blue-dot navigation system gives step-by-step directions without expensive equipment.
Many stores use mobile apps with indoor maps. These apps help customers plan their trips and locate items quickly. Turn-by-turn navigation and real-time promotions make the shopping experience smoother. A Google/Ipsos report found that 63% of smartphone users prefer stores that offer relevant product recommendations through mobile apps. This feature increases customer engagement and encourages more visits.
Indoor maps help customers find stores, restrooms, and exits.
Real-time promotions use geofencing to send offers when customers walk by certain products.
Crowd management analytics help stores organize aisles and reduce wait times.
Navigation tools support accessibility by helping customers with disabilities move around the store.
Retailers also benefit from these tools. Location data and proximity sensors improve store layouts and boost employee productivity. Customers enjoy a more convenient and stress-free shopping experience.
Smart Carts and Checkout

Automated Scanning
Smart carts and automated checkout systems change the way people shop for groceries. Many stores now use ai-powered smart carts that move with the help of motors and sensors. These carts can scan items as shoppers place them in the basket. This process reduces the need for manual scanning at the register. Shoppers with mobility or dexterity challenges find these features helpful because they do not need to push heavy carts or handle small barcodes.
Note: Remote control through smartphone apps lets users guide their carts with little physical effort.
The table below compares smart carts with traditional carts:
Feature/Aspect | Smart Cart (Remote Control) | Traditional Cart |
|---|---|---|
Control Method | Smartphone app with Bluetooth | Manual pushing |
Motors | Yes | No |
Sensors | Yes | No |
User Interaction | Remote via app | Physical/manual |
Purpose | Reduces physical effort, adds automation | Requires manual effort |
Customer satisfaction with smart carts reaches 80%, and engaged session rates are at 84%. These numbers show that automation makes grocery shopping easier and more enjoyable for many people.
Automated scanning also helps stores. Shelf-scanning robots can reduce out-of-stock items by more than 20%. Stores using predictive pricing and automated checkout see a 2% increase in sales and a 5% rise in profits. In 2018, grocers invested over $3.5 billion in robotics to improve efficiency.
Contactless Payment
Contactless payment systems add another layer of convenience. Shoppers can pay for their groceries by tapping a card or using a mobile wallet. This method speeds up the checkout process and reduces the need to handle cash or touch payment terminals. Self-checkout stations often include contactless options, making the process faster for everyone.
People with limited hand strength or mobility benefit from these systems. They do not need to swipe cards or enter PINs. Contactless payment also helps keep lines short, which improves the overall shopping experience.
Digital Grocery Store Technology
Online Shopping Platforms
Digital grocery store technology has changed how people shop for food. Online grocery shopping lets customers order from home or on the go. This saves time and money, especially for those who live far from stores or have trouble getting around. Many shoppers now use online platforms to avoid crowds, multitask, and use favorites lists for quick reordering. Delivery options help people in rural areas, food deserts, or those with physical challenges get the groceries they need.
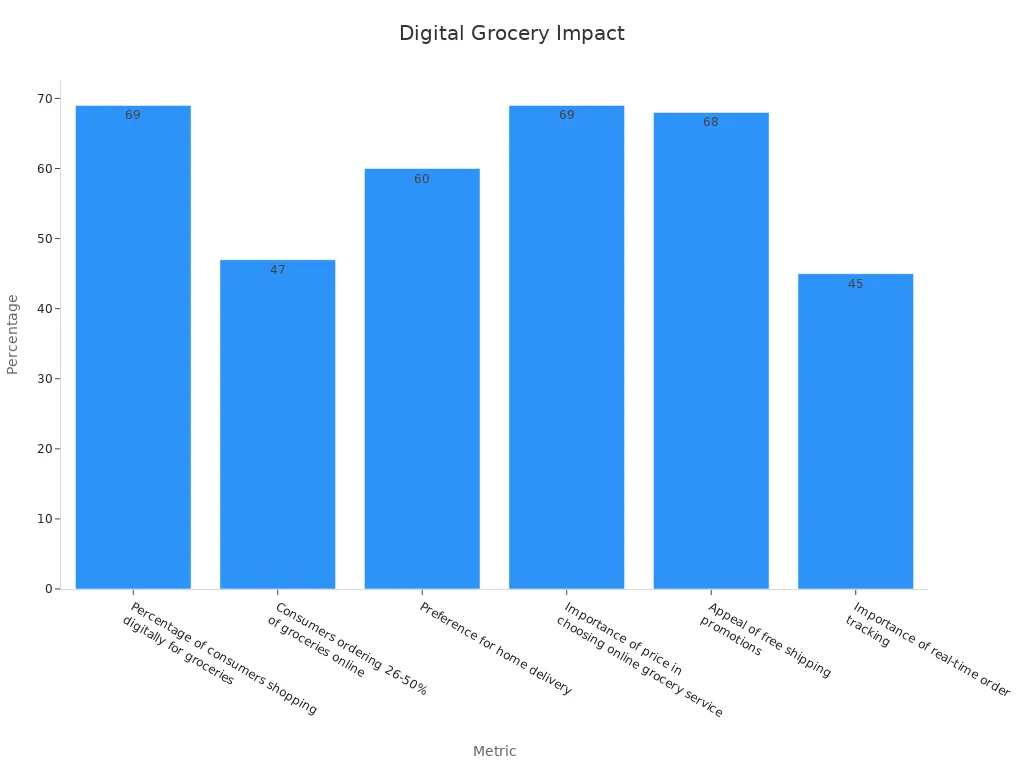
A growing number of shoppers prefer online grocery shopping because it is convenient and flexible. Surveys show that 69% of consumers shop for groceries online, and 47% order at least a quarter of their groceries this way. Home delivery appeals to 60% of shoppers, and free shipping promotions encourage more frequent orders. Price remains important, with 69% of people choosing services based on cost. Online food retail sales continue to rise as more people use digital tools for shopping.
Tip: Online grocery shopping can help older adults, people with disabilities, and busy families save time and effort.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Real-time inventory management plays a key role in online grocery shopping and delivery. Stores use advanced technology to track every item in stock. This helps avoid running out of popular products and reduces waste from overstocking. With live inventory data, stores can restock quickly and keep shelves full. Customers benefit from accurate order tracking and fewer canceled orders.
Real-time inventory management allows stores to monitor stock across all locations.
Automated systems help forecast demand and reorder products before they run out.
Barcode scanning and mobile apps speed up order processing and packing.
Accurate inventory records improve supply chain coordination and reduce delays.
Customers enjoy faster delivery and fewer mistakes in their orders.
Businesses lower costs by reducing errors, waste, and unnecessary storage.
Digital grocery store technology supports increased digital grocery sales by making inventory management more efficient. Online food retail sales grow as stores use these tools to meet customer needs for convenience, transparency, and fast delivery.
Accessibility Tools in Stores

Assistive Features
Many grocery stores now use digital tools to help all shoppers, especially those with disabilities. Features designed for people with disabilities often help everyone. This is called the "curb-cut effect." For example, sidewalk ramps help people with wheelchairs, but also parents with strollers or shoppers with carts. In the same way, digital assistive features like closed captions and audio descriptions make shopping easier for many people. Closed captions, once made for hearing-impaired users, are now used by up to 80% of viewers on popular platforms. Apple's devices include settings for vision, hearing, and motor needs, showing how technology can support a wide range of users. The BBC makes most of its shows accessible to people with vision loss by adding audio descriptions. These features remove barriers and help more people enjoy shopping.
Tip: Interactive signage and mobile apps in stores can guide shoppers to products, restrooms, or exits. These tools support people with visual or cognitive challenges and make the shopping trip smoother for everyone.
Inclusive Interfaces
Inclusive interfaces make digital shopping easier for all. About 15% of people worldwide live with a disability, so stores must design their websites and apps for everyone. Yet, only 3% of websites are accessible today. When companies use inclusive design, Microsoft found that usability improves by 30% for all users. Websites with accessible content see 35% more engagement. Simple changes, like better color contrast, can boost readability by almost half. These improvements help people with vision or learning differences, but they also make shopping faster and clearer for everyone.
Mobile apps with voice commands help people who cannot use touchscreens.
Multilingual options let shoppers choose their language.
Easy-to-read layouts and clear buttons help users with cognitive challenges.
Accessibility tools in stores and online make shopping more welcoming and efficient for all customers.
Transforming Supermarkets: Challenges and Future
Privacy and Security
Grocery stores collect large amounts of personal data to improve shopping experiences. This data helps stores offer personalized deals and faster service. However, it also creates privacy and security risks. Many companies store over 500,000 sensitive files, which increases the chance of data breaches. Only 62% of market research firms fully follow data protection rules. Most consumers expect strong data security, and 67% would switch brands if their data was mishandled.
Challenge Area | Statistic / Fact |
|---|---|
Compliance Gap | Only about 62% of market research firms fully comply with data protection standards. |
Consumer Expectations | 85% of consumers expect rigorous data security; 67% would switch brands after data mishandling. |
Ransomware Targeting | Retail is the 2nd most targeted industry for ransomware; 77% of organizations affected globally. |
IoT Device Vulnerabilities | 84% of enterprises use IoT devices; less than half have cybersecurity measures for them. |
Data Breach Cost | Average cost of cybercrime for organizations is $13 million per year. |
Retailers use AI and automation to lower the cost of data breaches. Strong encryption and access controls help protect customer information. Still, privacy concerns can affect trust and willingness to use new technology.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Not every shopper finds new technology easy to use. Some people, like older adults, may struggle with self-checkouts or mobile apps. The digital divide means that certain groups have less access or comfort with powered technology. Research shows that ease of use and usefulness are key for people to accept new tools. Stores must design systems that work for everyone, including those who are less tech-savvy.
Self-service checkouts and mobile apps can make shopping faster.
Some shoppers worry about privacy or do not understand how to use new features.
Augmented reality and AI offer more help but require consumer education.
Stores need to balance innovation with clear instructions and support.
By addressing these challenges, stores can make shopping more inclusive and accessible.
Future Trends
The future of grocery shopping will bring even more changes. Logistics as a Service (LaaS) will help stores deliver groceries quickly and reliably. AI will offer hyper-personalized recommendations, making shopping easier and reducing waste. The omnichannel approach will let customers shop online, pick up in-store, or use mobile discounts for a seamless experience. Automation and robotics will handle tasks like stocking shelves and packing orders.
Retail sustainability will become more important. Stores will use AI to cut food waste and switch to eco-friendly packaging. Platforms as a Service (PaaS) will help stores manage complex operations. The metaverse will allow shoppers to explore virtual stores, which will attract younger customers.
Recent forecasts show that eGrocery sales in the U.S. could reach $120 billion by 2028. Online grocery sales are growing much faster than in-store sales. As technology keeps transforming supermarkets, shoppers can expect more convenience, better service, and new ways to shop.
Powered technology continues to reshape the grocery experience for every customer. Stores use AI to improve inventory, reduce waste, and keep products available. Shoppers enjoy faster checkouts and easier store entry. Many customers find smart technology makes shopping simpler and more convenient.
AI-driven systems help stores deliver groceries on time and keep shelves stocked.
Smart checkout and payment tools reduce wait times and support accessibility.
Data-driven decisions let stores offer better promotions and product choices.
As these tools evolve, customers can expect even more improvements in convenience and value.
FAQ
What is powered technology in grocery stores?
Powered technology includes tools like AI, smart carts, and digital payment systems. These tools help shoppers find products, check out faster, and get personal recommendations.
How do smart carts help people with disabilities?
Smart carts use motors and sensors. Shoppers can control them with a phone app. People with mobility or dexterity challenges find it easier to shop without pushing heavy carts.
Are online grocery platforms safe to use?
Most online grocery platforms use strong security measures. They protect customer data with encryption and secure payment systems. Shoppers should use trusted websites and keep their passwords private.
Can older adults use digital grocery tools easily?
Many stores design apps and websites with simple layouts and large buttons. Some offer voice commands and help guides. These features make digital tools easier for older adults to use.
What should shoppers do if they need help in-store?
Shoppers can ask store staff for help. Many stores also offer mobile apps, interactive signs, or virtual assistants to guide customers to products or answer questions.
See Also
Transforming Retail Access Through Innovative Grocery Vending Solutions
The Future Of Retail Lies In AI-Driven Stores
Smart Technology Drives Change In Electronics Vending Retail
Modern Retail Advantages Of AI-Enabled Combo Vending Machines
Revolutionizing Online Store Management With AI E-Commerce Tools
