Shopping Cart Solutions: Pricing Models, ROI, and Implementation Costs

Business leaders often seek clarity on pricing models, ROI, and implementation costs before selecting shopping cart solutions. Making an informed decision matters because the right solution can transform an ecommerce business. Recent studies show that 90% of companies moving to scalable platforms experience significant revenue and sales growth. Shopping cart solutions that streamline payments, shipping, and inventory help prevent errors and maximize efficiency. With nearly 70% of shoppers abandoning carts, advanced features and targeted strategies can recover lost sales and boost profitability.
Key Takeaways
Choosing the right shopping cart solution boosts ecommerce growth by improving checkout, payments, and customer experience.
Subscription, modular, transaction-based, and free/open-source pricing models each have unique costs and benefits; businesses should pick based on their size and needs.
Investing in scalable and customizable platforms helps businesses grow smoothly and maximize return on investment over time.
Implementation costs include setup, customization, maintenance, and integration; understanding these helps avoid surprises and plan budgets effectively.
Avoid common pitfalls by focusing on user-friendly design, security, analytics, and future growth to ensure long-term ecommerce success.
Shopping Cart Solutions Overview

What Are Shopping Cart Solutions
Shopping cart solutions form the backbone of ecommerce software. These platforms allow businesses to manage sales, inventory, and marketing from a single dashboard. They support integrated payment processing, eliminating the need for third-party vendors. Most shopping cart solutions offer mobile-friendly templates and themes, which help stores look professional on any device. Businesses can use marketing, accounting, and shipping integrations to grow sales and streamline operations. Onboarding features, unlimited user support, and custom programming options make these platforms flexible for different business needs. Ease of use, quick setup, reliability, and technical support remain essential for successful ecommerce software.
Description | Market Position / Share Insights | |
|---|---|---|
Shopify | Cloud-based platform serving millions of businesses in 175 countries; integrated payments, shipping, marketing tools. | Market leader, widely used across top trafficked ecommerce sites. |
Adobe Commerce (Magento) | Open-source, highly customizable, targets enterprise-level businesses. | Strong presence in enterprise segment, less integrated than Shopify. |
WooCommerce | WordPress-based open-source platform, customizable but requires development resources. | Declined in rank but still widely used, especially among WordPress users. |
BigCommerce | Focuses on enterprise brands, robust built-in features, supports multichannel selling. | Maintains a steady but smaller market share compared to Shopify. |
Wix | Website builder with ecommerce capabilities, drag-and-drop store creation, limited ecommerce features. | Popular among smaller businesses, growing ecommerce functionality. |
Squarespace | Website builder with ecommerce tools, stylish templates, appeals to creatives and small businesses. | Similar to Wix, targets smaller ecommerce sellers. |
Importance for Ecommerce Businesses
Shopping cart solutions play a vital role in the success of ecommerce businesses. They simplify checkout, provide transparent pricing, and offer multiple payment options, which build trust with customers. User-friendly cart designs and streamlined processes encourage shoppers to complete purchases. Different cart types, such as pop-up, modal, full-page, and side panel, cater to various customer preferences. These features enhance user experience and increase conversion rates. Security measures like SSL certificates and trust symbols reassure customers and reduce drop-offs. Fast loading times and reliable checkout processes keep customers engaged and minimize frustration. Ecommerce software with robust analytics helps businesses understand customer behavior and tailor marketing strategies. Personalization through product recommendations and targeted promotions boosts conversion rates. Engagement features, such as reviews and Q&As, foster customer interaction and confidence. Shopping cart solutions act as a critical component of any ecommerce solution, driving operational efficiency and supporting business growth.
Pricing Models
Choosing the right pricing model for ecommerce software shapes the total cost of ownership and long-term business success. Each model offers unique advantages and challenges, especially when considering technology implementation, scalability, and ongoing costs. Below, the main pricing models are explained with real-world examples and cost breakdowns.
Subscription-Based
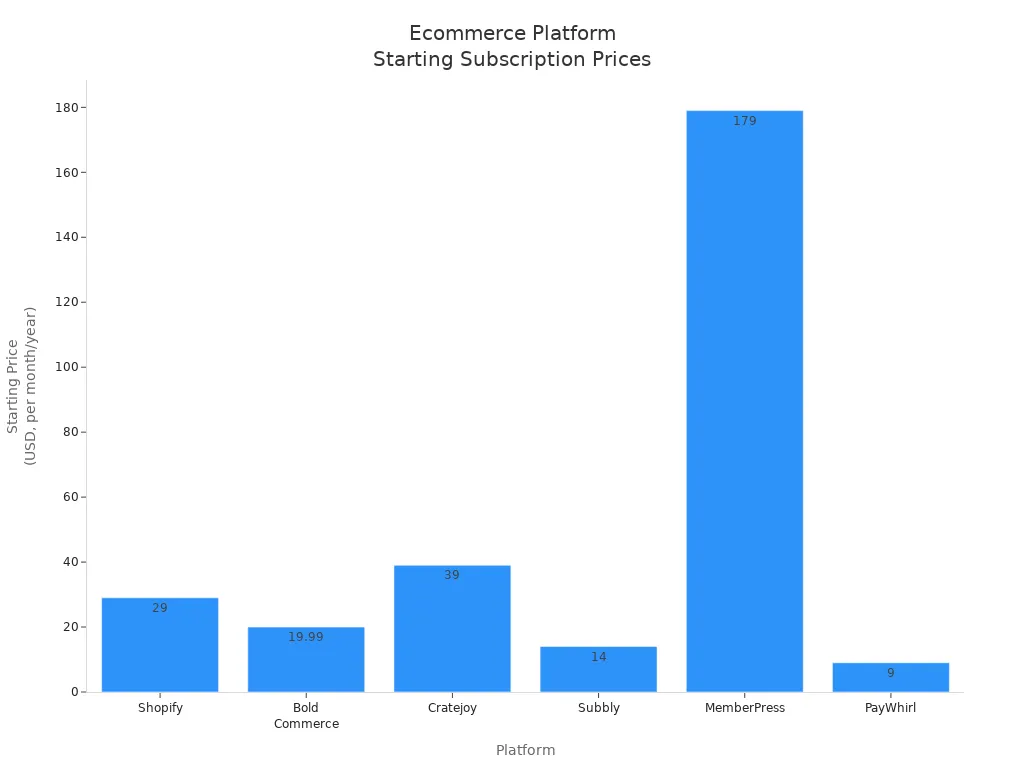
Subscription-based pricing remains the most popular model for ecommerce software. Merchants pay a fixed monthly or annual fee for access to a platform’s features, updates, and support. This approach simplifies budgeting and makes technology implementation predictable. For example, Subbly, designed for subscription businesses, starts at $29 per month and includes integrated checkout, multiple payment gateways, and tools for optimizing sales funnels. ThriveCart offers a one-time payment of $495 for lifetime access, eliminating recurring costs but requiring upfront investment.
Many leading platforms use this model. Shopify begins at $29 per month, targeting small and medium businesses. Payhip provides a free plan with a 5% transaction fee, a Plus plan at $29 per month with a 2% fee, and a Pro plan at $99 per month with no transaction fees. Platforms like Recurly and Chargebee offer custom pricing for enterprise clients, while Bold Commerce and Cratejoy serve niche markets with plans starting at $19.99 and $39 per month, respectively.
Plan Tier | Typical Monthly Cost Range | Target Users |
|---|---|---|
Free | $0 | Small startups, hobbyists |
Basic | $10 - $30 | Small businesses |
Intermediate | $35 - $100 | Growing businesses |
Advanced | $100 - $300 | Established businesses, SMEs |
Enterprise | Custom pricing | Large enterprises, high-volume sellers |
Subscription-based models help businesses plan for technology implementation and ongoing costs. They also provide flexibility to upgrade as the business grows.
Modular Pricing
Modular pricing allows businesses to select and pay only for the features they need. This model supports a custom approach to technology implementation, letting companies build a tech stack that fits their current requirements. For example, a business might start with basic ecommerce software and add modules for advanced analytics, marketing automation, or international shipping as it grows.
Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
Flexibility | Businesses can tailor their tech stack to current needs. |
Speed-to-market | New features can be tested and launched quickly. |
Scalability | Modules can be added or replaced as the customer base grows. |
Efficiency | Developers can improve individual modules without disrupting the whole system. |
Improved customer experience | Modular components enable personalized recommendations and real-time updates. |
A recent IDC survey found that 45% of global enterprise leaders use a composable front-end with a full-stack back-end, while 27% use fully headless and modular solutions. Enterprises value the ability to balance flexibility, speed, and cost-effectiveness. Modular pricing can lower technology implementation costs by reducing reliance on in-house expertise and allowing for gradual investment.
Transaction-Based
Transaction-based pricing charges a fee for each sale processed through the ecommerce software. This model aligns costs directly with sales volume, making it attractive for startups and small businesses with unpredictable revenue. However, for high-volume merchants, transaction fees can increase total costs significantly.
Platform | Transaction Fee Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Shopify | 0.5% to 2% | Fees depend on plan and payment processor. |
Squarespace Commerce | 3% on Business plan; waived on higher plans | Monthly plans from $26 to $46. |
Yahoo! Stores | 0.75% to 1.5% | Fees vary by plan; many features require paid apps. |
Etsy | 5% transaction fee + listing fees | $0.20 listing fee per item for 4 months; additional fees for payments. |
eBay | Around 10% of final sale price + listing fees | Fee structure depends on listings and category. |
Amazon | Referral fees + variable closing fees + $0.99 per item | Additional fees for fulfillment services; $39.99/month for professional sellers. |
Transaction fees typically range from 0.5% to 7%. For high-volume businesses, these costs can add up quickly. Subscription-based models with lower per-transaction rates often provide better value as sales increase. Technology implementation for transaction-based models requires careful monitoring to manage costs and optimize profitability.
Transaction-based pricing offers low entry costs but can become expensive as sales grow. High-volume sellers should analyze total cost carefully before choosing this model.
Free/Open-Source
Free or open-source ecommerce software appeals to businesses seeking to minimize upfront costs. Platforms like Magento Open Source, WooCommerce, Shopware, PrestaShop, Spree Commerce, Solidus, and nopCommerce offer flexibility and scalability. WooCommerce is especially popular among WordPress users, while Magento serves medium to large enterprises. nopCommerce powers over 65,000 live stores worldwide, supporting multiple business models and extensive customization.
However, free software does not mean zero cost. Technology implementation for open-source solutions involves several hidden costs:
Hidden Cost Category | Description & Examples |
|---|---|
Hosting | Merchants must pay for web hosting separately. |
Security & PCI Compliance | Additional investment in security measures is required. |
Customization & Add-ons | Essential features often require paid extensions, which may cause compatibility issues. |
Technical Support | Official support is limited; most help comes from community forums. |
Maintenance & Upgrades | Merchants handle manual upgrades and backups, increasing ongoing costs. |
Developer Costs | Installation and customization often require hiring developers. |
Software Limitations | Some platforms need extra investment to meet business needs. |
Free plugins like WooCommerce offer basic tools, but essential extensions can cost between $49 and $299. Magento Open Source requires investments in hosting, domains, SSL certificates, and paid add-ons. Hiring developers for setup and troubleshooting adds to the total cost. While open-source ecommerce software reduces licensing fees, the total cost of ownership can be substantial due to ongoing technology implementation and maintenance.
Note: Businesses should evaluate both visible and hidden costs before choosing a free or open-source solution. The right choice depends on store size, complexity, and available resources.
ROI Analysis

Cost vs. Benefit
Shopping cart solutions deliver measurable roi by reducing costs and increasing revenue. Many ecommerce brands see cost savings through automation, fewer manual errors, and improved checkout processes. For example, integrating sustainable options at checkout can boost conversion rates by 9% to 22%. Nuzet, a nutrition company, saw a 22% increase in conversions after adding a climate impact feature. Tribe Kelley experienced a 19% rise, and The Little Market gained a 9% boost. These improvements lead to higher average order value and more completed sales. Streamlined checkout, faster page loads, and fewer required steps also reduce cart abandonment, preserving high-value orders. Product bundling and page optimization encourage shoppers to add more items, which increases both revenue and cost savings.
The typical payback period for investment in shopping cart software ranges from 5 to 12 months. This means businesses often recover their initial investment within a year, making the return on investment attractive. Shorter payback periods signal strong marketing efficiency and product value.
Scalability
Scalability plays a key role in long-term roi. A scalable shopping cart solution handles more traffic and transactions as a business grows, without performance issues or extra costs. Cloud-based platforms offer flexible resources during peak seasons, reducing operational overhead and supporting cost savings. Integration with inventory, CRM, and marketing tools improves efficiency and customer satisfaction. Investing in scalable technology early helps avoid expensive upgrades later, protecting long-term savings and roi.
Long-Term Value
Long-term value comes from tracking the right metrics. Businesses should monitor customer lifetime value, retention rate, repeat purchase rate, and average order value. High retention and repeat rates show strong customer loyalty, which leads to ongoing cost savings and higher roi. Reducing cart abandonment and optimizing the checkout process also support long-term revenue growth. Shopping cart solutions that support lifecycle marketing, loyalty programs, and personalized experiences help businesses maximize their investment and sustain profitability over time.
Implementation Cost Breakdown
Setup and Configuration
Setup and configuration form the foundation of technology implementation for shopping cart solutions. Businesses must consider the initial implementation cost, which includes licensing, installation, and basic system setup. Most platforms offer guided onboarding, but advanced configuration often requires expert support. The total cost of ownership starts with these upfront expenses. For small businesses, setup costs may range from $5,000 to $25,000 on DIY platforms. Enterprise solutions can reach $300,000 to $500,000, depending on the platform and required features.
Key setup components include:
Licensing fees for software access
Hosting costs for cloud or on-premises infrastructure
Domain registration and SSL certificates for security
Basic data migration from legacy systems
Tip: Investing in premium cloud infrastructure can increase annual costs but ensures reliability during high transaction periods.
Customization
Customization drives the flexibility and uniqueness of ecommerce software. The implementation cost rises as businesses demand more tailored user experiences, unique workflows, and brand-specific features. The total cost of ownership reflects these choices, especially when custom design and integrations are involved.
Customization Aspect | Description | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
User Experience Design | Minor tweaks to templates or full custom design and studies | |
Functionality & Features | Unique workflows and brand-specific features | Included in design/customization costs but can significantly raise expenses |
Integrations | Custom data mappings and business rules for syncing with existing systems | $50,000 to $150,000+ depending on data cleanliness and complexity |
Payment Gateways & Security | Out-of-the-box security measures and payment processing fees | 3% to 4% of order totals (ongoing costs) |
Platform Selection | Choice of platform affects licensing and base costs | Varies by platform; DIY platforms $5,000-$25,000; Enterprise $300,000-$500,000 |
The table above shows that extensive customization, especially in user experience design and integration, can dramatically increase the total cost. Businesses must weigh the benefits of unique features against the impact on total cost of ownership.
Maintenance
Maintenance ensures the long-term performance and security of shopping cart solutions. Routine cleaning, wheel repairs, frame repairs, and anti-theft system maintenance all contribute to operational costs. Choosing wire shopping carts over plastic ones can reduce annual maintenance costs by 20%. IoT technology in carts helps minimize maintenance by optimizing battery usage and reducing data transmission, which extends battery life and lowers costs.
Maintenance Component | Cost Range per Cart (Annual) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Routine Cleaning | $5 - $10 | Prevent rust and maintain hygiene |
Wheel Repairs | $10 - $30 | Needed every 1-2 years |
Frame Repairs | $20 - $100 | Welding or replacement varies by material |
$5 - $15 | For electronic locks | |
Fleet-wide Maintenance | $1,500 - $5,000 | For 100 carts |
Ongoing maintenance and minor changes help businesses keep pace with industry evolution. The total cost of ownership includes these recurring expenses, which can be part of a subscription or billed separately. For retail price optimization software, maintenance is often bundled with technical support and upgrades.
Integration
Integration connects shopping cart solutions with payment gateways, third-party services, and backend systems. The implementation cost for integration varies based on complexity, customization needs, and technical expertise. Some platforms offer plugin-based or built-in integrations, which reduce total cost for businesses with limited technical skills. Custom integration services can cost from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on checkout flows, multi-currency support, and advanced analytics.
Payment Gateway | Type | Typical Transaction Fees |
|---|---|---|
PayPal | Hosted | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
Stripe | Integrated | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
Square | Integrated | Approximately 2.6% + $0.10 |
Authorize.Net | Integrated | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
2Checkout (Verifone) | Hosted | Higher fees: 3.5% + $0.35 |
Worldpay | Integrated | Custom pricing |
Braintree | Integrated | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
Adyen | Integrated | Custom pricing |
Amazon Pay | Hosted | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
Shopify Payments | Integrated | Approximately 2.9% + $0.30 |
Third-party services and SaaS platforms often provide developer-friendly APIs and SDKs, making integration easier and reducing technology implementation barriers. However, advanced integrations for unique business needs can increase the total cost of ownership.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Typical Cost Ranges
The total cost of ownership for retail price optimization software includes acquisition, operating, and retirement costs. Acquisition covers licensing, implementation, integration, and training. Operating costs include ongoing maintenance, technical support, and upgrades. Retirement costs involve decommissioning and disposal. Businesses must consider all these phases for accurate tco calculation.
Cost Component | Description | Cost Range / Notes |
|---|---|---|
Implemented Solution | Pricing based on Revenue Under Management (RUM) on a sliding scale | Cost increases with RUM; notification before price adjustment |
Cloud Infrastructure | Premium hosting for specific needs like high transactions or delayed upgrades | Annual premium cost beyond basic installation |
Price Optimization | AI-driven price optimization features included in Price and Profit packages | Included but affects overall cost |
On-Going Maintenance | Maintenance and minor changes to keep pace with business and industry evolution | Ongoing cost included in subscription |
Training | Customized training to help users adapt and maximize software use | May be included or premium depending on package |
Technical Support | Standard support included; premium support (e.g., pricing scientists) available for complex needs | Premium support increases cost; useful for complex pricing scenarios |
Subscription Cost Range | Basic starter package | Approximately $100,000 |
Subscription Cost Range | Full suite with advanced features and premium support | Up to $3.5 million or more, depending on scale and features |
The total cost of ownership can range from $100,000 for basic packages to $3.5 million or more for advanced solutions. Businesses should analyze all implementation costs, operational costs, and ongoing expenses to understand the full financial commitment. Accurate tco calculation helps leaders make informed decisions and plan for future growth.
Note: Reviewing all components of implementation cost, including setup, customization, maintenance, and integration, ensures a realistic view of total cost and supports long-term business success.
Choosing Ecommerce Software
Assessing Needs
Selecting the right ecommerce software begins with a thorough assessment of business needs. Companies must identify their business model, whether B2B, B2C, or hybrid, and consider the type of products they sell. Digital goods require instant downloads, while physical products need inventory and shipping management. Understanding the target audience helps tailor the shopping experience, including mobile responsiveness and payment options. Forecasting future growth ensures the platform can scale and adapt to new markets. Businesses should also evaluate integration capabilities, such as data volume management and efficient API interfaces. Security compliance, including GDPR and PCI DSS standards, remains essential for protecting customer data.
Explanation | |
|---|---|
Multi-channel Support | Ability to sell across multiple marketplaces, social media, and omnichannel strategies. |
Personalization | Smart product recommendations and targeted marketing to enhance customer experience. |
Customization Options | Tailoring storefront, branding, checkout, shipping, promotions, and third-party integrations. |
Payment Processing | Support for multiple payment methods and currencies to cater to diverse customers. |
PCI Compliance | Ensures secure handling of credit card data, builds trust, and meets legal requirements. |
Scalability | Platform can grow with business, handling more products, traffic, and sales without performance loss. |
Security | Robust features like SSL encryption, PCI compliance, and regular updates to protect data. |
Analytics and Reporting | Tools to analyze customer behavior, sales, and optimize store performance. |
Integration Capabilities | Support for third-party apps and APIs for order, inventory, marketing, and social media tools. |
SEO | Optimizing site for organic traffic and competitive advantage. |
Customer Support | Reliable, multi-channel support with knowledgeable teams. |
Transparent Pricing | Clear and understandable pricing structures. |
User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive for customers and easy admin panel for marketers without heavy IT reliance. |
Responsive Design | Website performs well across devices (mobile, tablet, desktop). |
Comparing Features
Feature sets differ widely among ecommerce platforms. Large enterprises often choose solutions like Salesforce B2B Commerce Cloud or SAP Commerce Cloud for advanced catalog management, AI automation, and deep integration. These platforms offer scalability and customization but require technical expertise and higher investment. Mid-sized businesses may prefer CS-Cart Ultimate or X-Cart, which provide rich B2B features and easier usability. Commercetools stands out for enterprises needing agility and composability. Adobe Commerce (Magento) supports both B2B and B2C models with omnichannel capabilities. Companies should compare platforms based on business size, industry focus, and required features.
Platform | Business Size Suitability | Industry/Use Case Focus | Key Features & Strengths | Limitations & Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Salesforce B2B Commerce Cloud | Large enterprises | Complex B2B cycles, large organizations | Advanced catalog management, AI-powered automation, personalized experiences, deep Salesforce integration | High cost, complex customization, requires technical expertise, challenging third-party integrations |
CS-Cart Ultimate | Small to large wholesalers & manufacturers | Wholesalers, manufacturers, niche marketplaces | Highly customizable, supports unlimited sellers/storefronts, rich B2B features (custom pricing, multi-user accounts, quote management) | Self-hosted, requires some technical knowledge, but accessible for non-technical users as well |
Commercetools | Enterprises | Enterprises needing agility and composability | Headless, API-first, cloud-native, supports multiple storefronts and brands, rapid integration | Primarily suited for enterprises, may require development resources |
SAP Commerce Cloud | Large enterprises | Complex B2B workflows, innovation at scale | Highly configurable, scalable, deep enterprise system compatibility | Enterprise-level complexity and cost |
Adobe Commerce (Magento) | Enterprises | Diverse customer segments, B2B & B2C | Advanced customization, omnichannel support, scalable | Requires technical expertise, potentially high maintenance costs |
X-Cart | Small to mid-sized businesses | General B2B and B2C | Cloud and downloadable options, vendor management, payment distribution, syncs with business systems | Lacks some B2B-specific features, multiple storefronts need customization, mixed reviews on support |
3dcart | Small to mid-sized B2B customers | General B2B | Most must-have B2B features except multiple storefronts and advanced price list management | Poor customer service reported, which can impact business operations |
Avoiding Pitfalls
Many businesses encounter pitfalls when choosing ecommerce software. Companies sometimes select big brand carts without assessing fit, resulting in unnecessary expenses for unused features. Focusing only on upfront costs and ignoring transaction fees can lead to higher long-term costs. Some overlook back-end analytics, missing valuable insights for growth. Complicated multi-page checkouts increase cart abandonment. Neglecting security badges and mobile optimization can reduce customer trust and exclude mobile shoppers. Businesses should avoid underestimating total costs, ignoring customer service quality, and choosing platforms that lack scalability.
Tip: Always verify security compliance, prioritize user-friendly interfaces, and ensure the platform supports future growth.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
Overlooking transaction fees.
Neglecting analytics and reporting.
Using complex checkout processes.
Missing security badges and trust signals.
Choosing non-mobile-friendly solutions.
Ecommerce businesses must weigh both short-term and long-term factors when selecting a shopping cart solution. Immediate needs include cost-effectiveness and quick setup, while long-term goals focus on durability, brand image, and ongoing savings. The table below highlights these considerations:
Short-Term Focus | Long-Term Focus |
|---|---|
Quick turnaround | Durability, safety, brand image |
Lower initial total cost | Greater savings, lower total cost of ownership |
To maximize ROI, companies should:
Review all cost components, not just upfront fees.
Prioritize scalability and user experience.
Choose ecommerce software that supports future growth.
FAQ
What is the main difference between shopping cart solutions and ecommerce software?
Shopping cart solutions focus on checkout and payment processes. Ecommerce software covers the entire online store, including product management, marketing, and analytics. Both tools help businesses sell products online and improve customer experience.
How do businesses estimate the total cost of ownership for shopping cart solutions?
Businesses calculate total cost of ownership by adding setup, customization, maintenance, integration, and subscription fees. They also include costs for training, support, and upgrades. This approach helps companies plan budgets and avoid unexpected expenses.
Can shopping cart solutions integrate with existing business systems?
Most shopping cart solutions offer integration with payment gateways, inventory tools, and marketing platforms. Many ecommerce software options provide APIs or plugins for easy connection to other business systems, which streamlines operations and data management.
Why is scalability important in ecommerce software?
Scalability allows ecommerce software to handle more products, customers, and sales as a business grows. This feature prevents slowdowns and ensures a smooth shopping experience during busy periods, supporting long-term business success.
How do shopping cart solutions help reduce cart abandonment?
Shopping cart solutions use features like fast checkout, mobile optimization, and trust signals to encourage customers to complete purchases. These tools address common reasons for cart abandonment and help businesses recover lost sales.
See Also
Detailed Cost Analysis Of Vending Machines And Their Features
Transforming Online Store Management With AI-Powered E-Commerce Tools
Key Features Influencing Vending Machine Pricing And Costs
Starting An AI-Driven Corner Store With Low Initial Investment
What Retailers Should Understand About The Growth Of AI Corner Stores
