Shopping Carts: From Traditional Retail to Smart Mobile Solutions

Shopping carts have changed dramatically, moving from basic wire frames to smart devices that use advanced technology. Retailers now invest in smart solutions to improve both the shopping experience and store efficiency.
Market growth shows a shift to digital carts with features like barcode scanning and real-time data.
Smart shopping carts give shoppers quick checkouts, personalized offers, and instant information.
These changes highlight how technology reshapes shopping and retail operations.
Key Takeaways
Shopping carts evolved from simple metal frames to smart devices that speed up shopping and improve store efficiency.
Smart carts use AI, sensors, and screens to help shoppers track items, get personalized offers, and pay quickly without waiting in line.
Retailers benefit from smart carts by reducing labor costs, managing inventory better, and increasing sales through personalized marketing.
High costs and privacy concerns slow smart cart adoption, but technology advances and strong data protection will boost acceptance.
Future smart carts will use AI and automation to offer even more personalized, fast, and enjoyable shopping experiences.
Origins of Shopping Carts

Early Purpose
The rise of self-service grocery stores in the early 1900s changed how people shopped. Clarence Saunders opened the first self-service grocery store in 1916. Shoppers could now pick their own items from the shelves. As grocery stores grew larger and offered more products, customers faced a new problem. Carrying heavy baskets made shopping difficult, especially when buying many items. Store owners noticed that shoppers would stop shopping when their baskets became too full or heavy. This limited how much they could buy.
The invention of shopping carts solved this problem. Sylvan Goldman, a grocery store owner, saw that customers needed a better way to carry more goods. In 1937, he created a device that allowed shoppers to move easily through the grocery aisles and carry more products. His goal was to make shopping more comfortable and to help people buy more items in one trip.
First Designs
Goldman’s first cart design looked like a folding chair with wheels. It held two wire baskets, one above the other. Shoppers could push the cart and fill both baskets as they moved through the grocery store. At first, many people did not want to use the cart. Some women thought it looked too much like a baby carriage. Others did not see why they needed it. Goldman hired actors to show how easy and helpful the cart could be. He also placed greeters at the store entrance to explain its benefits.
Retailers who used the cart soon noticed a change. Stores like Sears saw higher sales because shoppers could carry more items. The cart quickly became a common sight in grocery stores. Over time, new features like child seats and swivel wheels made the cart even more useful. The early designs set the stage for the modern shopping carts seen in grocery stores today.
Cart Evolution
Materials and Features
The materials used in grocery cart construction have changed a lot since the first designs. Early grocery carts were made entirely from metal, mainly steel, because it was strong and could hold heavy loads. These carts weighed about 70 pounds and had wire baskets. Over time, new materials made carts lighter and easier to use.
In the 1940s, grocery stores started using plastic parts in carts. This change made each cart 15 to 20 pounds lighter and helped prevent rust.
Modern grocery carts often use a mix of plastic baskets made from FDA-approved resin and steel frames. These carts weigh about 17.73 kg and last longer.
Many stores now use recycled polypropylene in their carts. This material helps protect the environment and keeps the cart strong.
Some grocery carts have modular designs, making repairs and upgrades simple.
New features like built-in scanners and screens help shoppers check prices and find products quickly.
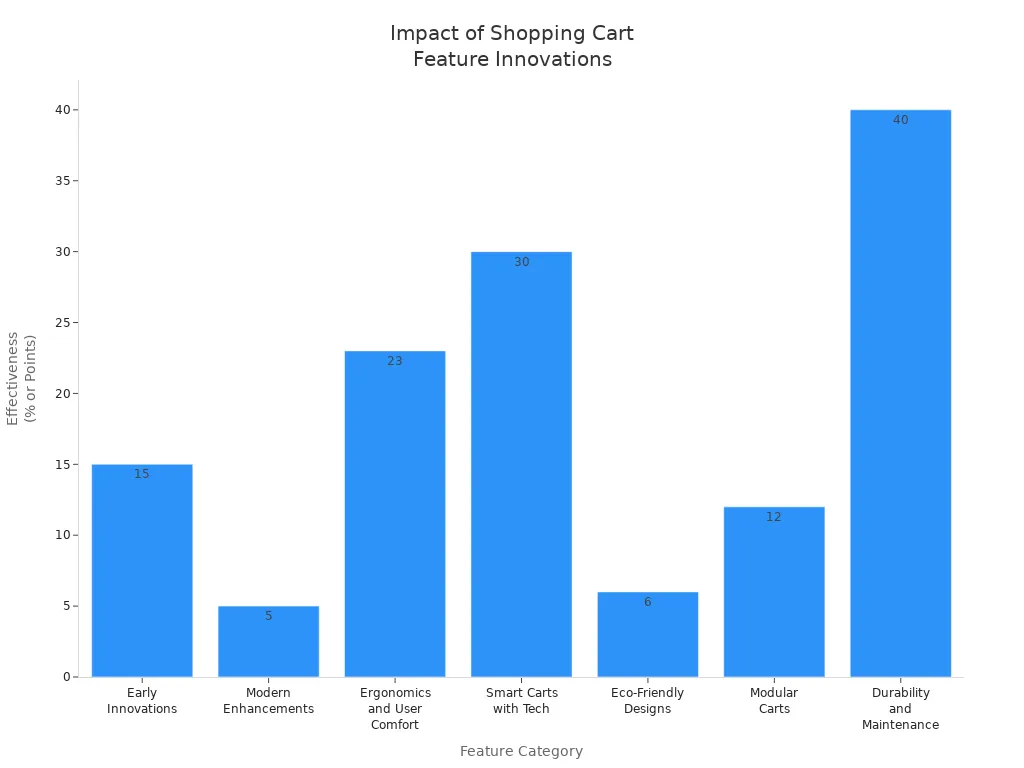
Feature Category | Specific Innovations/Features | Evidence of Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
Early Innovations | Nested frames, child seats, rubber-bonded casters | 15% increase in basket sizes due to sturdier, easier-to-maneuver carts |
Modern Enhancements | Lightweight plastic shells, anti-theft locking wheels, RFID tags | Reduced user friction and longer cart lifespan (5 years longer than chrome wire) |
Ergonomics and User Comfort | Handle angle adjustments, elastic pushback handles | 23% reduction in forearm fatigue; 13% longer shopping time; 8% higher basket value |
Smart Carts with Technology | Computer-vision cameras, weight sensors, handle-mounted screens | 30% reduction in queue times; increased basket sizes due to real-time subtotals |
Eco-Friendly Designs | Recycled plastics, bio-based handles | 6-point brand trust increase among eco-conscious shoppers |
Modular and Customizable Carts | Snap-on racks, category-specific attachments | 12% increase in average spend in specialty stores |
Durability and Maintenance | Duplex-powder coatings, UV-stabilized plastics, modular parts | 40% reduction in maintenance labor; 33% lower replacement costs over 5 years |
In-Store Impact
Grocery cart innovations have changed how people shop and how stores operate. Smart carts with touchscreens, barcode scanners, and weight sensors make shopping faster and more fun. Shoppers can check prices, see offers, and get product details right from the cart. These features help save time and often lead to more impulse buys.
Smart carts improve convenience and encourage shoppers to return to the store.
Larger grocery stores with smart carts see higher customer satisfaction.
Real-time information from carts helps shoppers make better choices and finish shopping quickly.
Smart carts also help stores track inventory and understand what customers want.
Retailers use data from grocery carts to adjust store layouts and product placement. AI-powered analytics show that shoppers prefer smaller carts, so stores design aisles for easier movement. This change led to a 20% increase in sales and a 25% boost in product discoverability. Stores also use cart data to place popular items in high-traffic areas and group related products together. These strategies help increase basket size and improve inventory management. By studying cart and shopper data, grocery stores can predict demand and adjust their inventory, making shopping smoother for everyone.
Digital Shift
Online Shopping Carts
Online shopping carts have changed how people buy products on the internet. These carts use technology to let shoppers select, review, and manage items before checkout. Unlike traditional carts, online carts are software tools that offer many features:
The cart supports different payment methods, such as credit cards and mobile wallets.
Stores can add special offers, coupons, and shipping options.
Businesses can use different types of carts, like quote carts, which allow custom pricing and flexible payment terms.
Traditional carts are simple and physical. They help people carry items in stores. Online carts, powered by smart technology, give shoppers more control and information. They also help stores track what customers want and offer a more personal experience.
Note: Online shopping carts make it easy for people to shop from anywhere, using computers or mobile devices. This flexibility has helped e-commerce grow quickly.
E-Commerce Changes
The rise of online shopping carts has driven big changes in e-commerce. Technology now lets stores track inventory in real time and update stock as people add items to their carts. Automated checkout systems reduce the need for cashiers and speed up the buying process. Smart carts use AI to suggest products, remind shoppers about abandoned carts, and offer dynamic pricing.
Major Change | Explanation |
|---|---|
Real-time inventory tracking and faster checkout | |
Loss Prevention | Item recognition reduces theft and errors |
Online-Offline Integration | Carts sync with digital profiles for a seamless shopping journey |
Personalization | AI-powered recommendations and gamification increase engagement |
Shopping Experience | Combines convenience of e-commerce with benefits of physical stores |
Almost 70% of online shopping carts are abandoned, costing stores billions each year. High costs, complicated checkouts, and security worries cause many shoppers to leave items behind. Still, smart carts support mobile payments, buy now pay later options, and work across devices. Mobile wallets are expected to handle over half of all e-commerce transactions by 2026. As technology improves, smart carts will keep making shopping easier and more personal.
Smart Carts
AI and Sensors
Smart carts use advanced technology to change how people shop. Artificial intelligence powers many features in these carts. Cameras, sensors, and digital scales work together to recognize items as shoppers place them in the cart. This system removes the need for manual barcode scanning. The cart’s screen shows real-time spending, personalized offers, and product recommendations. Some carts even help shoppers find items in the store using GPS navigation.
Smart shopping carts like Instacart’s Caper Carts use AI to give real-time suggestions and create fun shopping experiences. Retailers such as Kroger and Sam’s Club use AI to make checkout faster and prevent theft. These carts sync with shopping list apps through QR codes, making it easy to check off items. Payment happens right on the cart, so shoppers can skip the checkout line. Gamification features, like coupon wheels, make shopping more engaging.
Sensors such as RFID and object detection help the cart identify products instantly. This technology automates billing and updates inventory in real time. The process reduces checkout lines and makes shopping smoother. Sensors also help stores manage inventory by tracking what goes into each cart. The carts are durable, weather-resistant, and have long battery life. GPS tracking and wheel locks prevent theft and keep carts within store boundaries.
The smart cart market is growing quickly. Many factors drive this growth:
More people want contactless shopping, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic.
AI and IoT integration allow automatic billing, navigation, and real-time inventory tracking.
Retailers invest in smart cart technology to improve efficiency and customer experience.
Hypermarkets and supermarkets expand their use of smart carts.
North America leads the market because of high demand for contactless shopping and rapid adoption of retail automation.
Major retailers like Walmart, Carrefour, and 7-eleven use smart carts to boost efficiency.
The smart cart market is expected to grow from $1.72 billion in 2024 to $2.21 billion in 2025, reaching $5.35 billion by 2029.
Examples like Snapcart and Cust2Mate show how smart carts work in real stores. Cust2Mate uses sensors and a real-time platform to reduce physical contact by 95%. Customers spend 20% more and receive personalized ads based on their location in the store. These solutions operate with edge computing, which keeps data private and the system scalable. Amazon’s Dash Cart and Carrefour’s RFID-enabled carts also show how smart cart technology improves convenience and efficiency.
Self-Checkout Integration
Smart carts make self-checkout easy and fast. Shoppers place items in the cart, and the technology recognizes each product. The cart tracks everything and processes payment automatically. This system removes the need for manual scanning or waiting in line. RFID and AI work together to monitor item selection and automate billing. Customers can leave the store without stopping at a traditional checkout.
Surveys show that most people prefer self-checkout. About 73% of shoppers like using self-checkout, and 85% believe it is faster than regular checkout. The self-checkout market is growing quickly, expected to reach $12.01 billion by 2029. Smart carts help stores manage lines by sending real-time data to managers. If lines get long, the system alerts staff to open more registers or guide shoppers to less busy areas. This technology supports frictionless checkout and improves efficiency for both shoppers and retailers.
Early smart cart solutions combined RFID with barcodes to speed up checkout. Now, AI and computer vision make the process even faster. Shoppers enjoy frictionless checkout, which means they can finish shopping and pay without any delays. Retailers benefit from reduced labor costs and better customer satisfaction.
IoT and Connectivity
IoT, or the Internet of Things, connects smart carts to store systems. Sensors like RFID readers, barcode scanners, and cameras collect data on every item placed in the cart. Weight sensors check the number of items and help prevent theft. Proximity sensors track the cart’s movement and support navigation and personalized promotions.
IoT connectivity links these sensors to central inventory systems. This connection allows real-time updates of stock levels and sends restocking alerts to staff. The technology helps reduce shrinkage by tracking product movement. Retailers use the data to learn about customer behavior and improve marketing. Shoppers get a seamless checkout experience and better product availability.
Smart cart technology uses Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or 5G to send data to cloud or edge platforms. AI and machine learning analyze this data to offer personalized promotions and improve store operations. Customer touchpoints, such as mobile apps and kiosks, deliver information directly to shoppers. Real-world examples include Amazon Go’s cashier-less checkout and Walmart’s smart inventory management. These solutions improve inventory accuracy, operational efficiency, and the overall shopping experience.
Smart carts address many problems found in traditional carts. They reduce wait times, improve efficiency, and make shopping more enjoyable. The technology behind these carts continues to evolve, offering modular upgrades and new features. As more retailers adopt smart cart technology, both shoppers and stores benefit from a faster, smarter, and more connected shopping journey.
Shopping Experience
Customer Benefits
Smart shopping carts have transformed the grocery shopping experience for customers. These carts use RFID technology and IoT features to identify products automatically. Customers receive real-time updates on their cart contents, which helps them keep track of spending and avoid surprises at checkout. Touchscreen displays and mobile apps give customers product information, easy payment options, and bill details. This technology speeds up the shopping process and makes it more convenient.
Customers enjoy a seamless experience by combining shopping, bagging, and checkout into one step.
Sensor-based systems guide customers to products and offer personalized recommendations.
Decision tree algorithms help classify shopping lists and provide accurate discounts.
Blockchain and biometric security measures protect transactions and add a layer of personalization.
Customers can receive e-bills and access purchase details online, making post-shopping tasks easier.
Smart carts merge the convenience of online shopping with the benefits of physical stores. This approach improves customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Research shows that real-time spending feedback from smart carts affects customer satisfaction in different ways. Budget-conscious customers often increase their spending and plan to return, while others adjust their habits without feeling less satisfied. Kroger saw a 30% rise in customer satisfaction after using smart carts that reduce checkout times and offer personalized recommendations. Aldi improved customer satisfaction by using autonomous checkout technology, which led to shorter wait times. Sam’s Club Scan & Go users reported a 27% increase in basket size and faster checkout. These results show that smart carts make the shopping experience faster, more personal, and more enjoyable for customers.
Retailer Advantages
Retailers gain many benefits from smart shopping carts. These carts create interactive shopping experiences that increase customer spending by 20%. Contact between staff and customers drops by 95%, which improves safety and efficiency. Real-time product and customer flow management helps stores adapt quickly to changes, such as sudden demand spikes or security issues.
Checkout queues disappear because customers pay directly on the cart.
Personalized ads and item suggestions reach customers based on their location in the store.
In-store navigation based on shopping lists improves convenience and store flow.
Integration with existing POS systems streamlines retail operations.
Smart carts scale easily, allowing quick updates across multiple stores.
Smart carts also reduce checkout wait times by enabling automated payment processing and digital receipts. Inventory management improves through real-time data collection and AI-powered product detection. Labor costs drop as manual checkout and inventory tasks become automated. Retailers gain valuable data on customer behavior, which helps them optimize marketing strategies and improve customer loyalty. AI technologies like YOLOv8 boost product detection accuracy, making the shopping experience smoother.
Aspect | Impact on Store Efficiency and Sales Conversion |
|---|---|
Reduction in Stock-Outs | 67% fewer stock-outs due to real-time inventory management, improving product availability and reducing lost sales opportunities. |
Labor Cost and Reconciliation Time | 50% reduction through automation of restocking notifications and maintenance alerts, allowing staff to focus on strategic tasks. |
Sales Conversion and Performance | 15% increase in sales performance attributed to streamlined checkout and personalized offers. |
Average Transaction Value | 38% increase driven by AI-driven personalized recommendations encouraging customers to add more items. |
Revenue per Square Foot | Up to 20% increase by optimizing product placement and shelf replenishment using data collected from smart carts. |
Productivity and Space Usage | 25% productivity gain and 20% better space utilization through inventory management integration. |
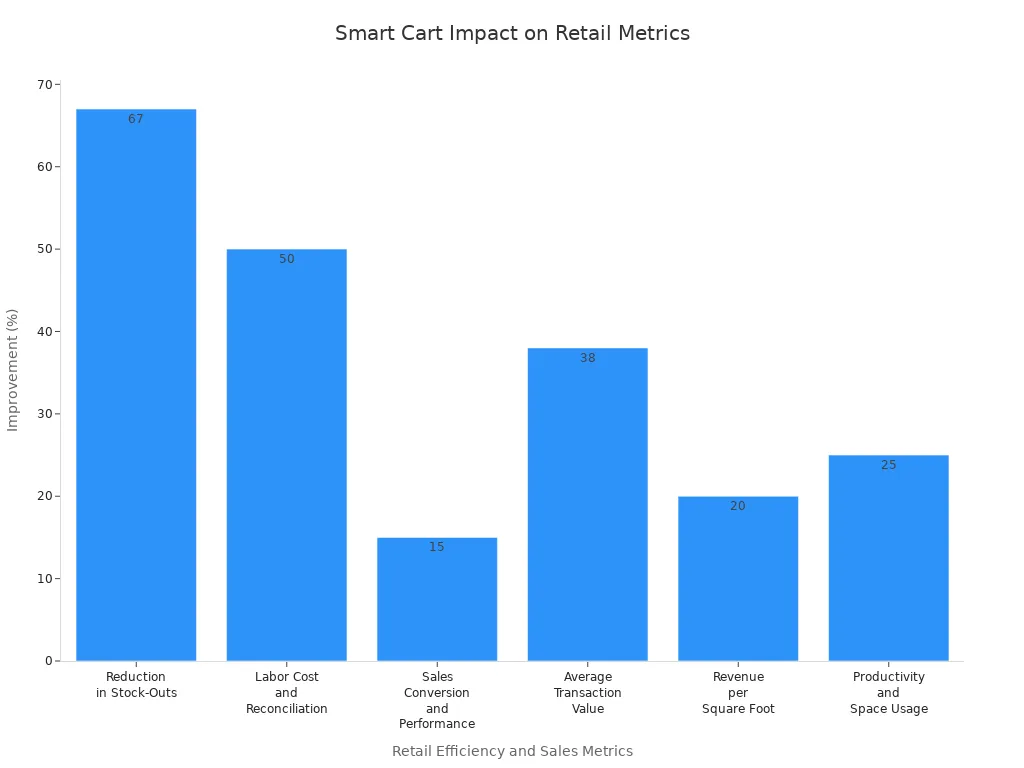
Smart carts automate routine tasks like restocking alerts and maintenance notifications. This automation reduces labor costs and reconciliation time by half. Integrated payment systems remove long lines and lower cart abandonment, which increases sales conversion rates. AI-driven personalization encourages customers to add more items, raising average transaction values by 38%. Navigation assistance helps customers find products quickly, which improves the shopping experience and builds customer loyalty. Data from smart carts allows retailers to optimize inventory management and store layout, further boosting operational efficiency and revenue.
Challenges and Costs
Despite many benefits, smart shopping carts present some challenges and costs for both retailers and customers. High initial investment costs make it hard for small and mid-sized retailers to adopt this technology. Integration with existing store infrastructure and legacy systems often requires extra spending on technology and staff training.
High upfront costs deter 56% of small retailers from adopting smart carts.
About 49% of retailers face integration and compatibility issues with legacy POS systems.
Staff training is a challenge, with 44% of stores needing comprehensive programs to use smart cart features.
Nearly 61% of small retailers cite high procurement and maintenance costs as a main barrier.
49% of decision-makers feel unsure about immediate returns on investment, which delays deployment.
Approximately 57% of retailers struggle with software compatibility between smart carts and existing systems.
Around 43% of staff need extra support to operate smart carts effectively.
Privacy and data security concerns also affect adoption. About 34% of consumers hesitate to use AI-powered shopping assistants because of privacy worries. Only 13% of Americans trust AI shopping assistants completely. Many consumers fear misuse of their data and lack of transparency. These concerns slow down the adoption of smart shopping carts. Experts believe that widespread consumer comfort with smart carts will take three to five years, depending on how well retailers balance convenience with strong data privacy protections.
Privacy concerns impact adoption because smart carts collect sensitive personal data, such as purchase history. Retailers must maintain data security and customer trust. Some stores, like Wegmans, have stopped using scan-and-go services due to theft and data security issues. This example shows how privacy and security concerns can directly affect the acceptance and continued use of smart cart technologies.
Note: While smart carts offer many advantages, retailers must address privacy, cost, and social interaction concerns to ensure a positive shopping experience for all customers.
Future Trends
AI and Automation
AI and automation are shaping the next generation of smart shopping carts. These carts use AI-driven hyper-personalization to offer tailored product recommendations and dynamic storefronts that adapt to each customer. Voice commerce integration lets customers search for products or reorder items using assistants like Alexa. Virtual try-ons and AR experiences help customers visualize products, which reduces hesitation and returns. Advanced predictive analytics optimize inventory and demand forecasting, ensuring the right products are always available. Multi-agent AI systems coordinate pricing, customer behavior, and inventory management in real time. No-code AI tools and increased platform integrations make these solutions more accessible to retailers. Companies like Amazon and H&M already use these technologies to improve the shopping journey.
Customer Engagement
Smart shopping carts are changing how customers interact with stores. Predictive analytics allow retailers to offer real-time promotions and recommendations, improving satisfaction and efficiency. Self-checkout features let customers scan and pay for items directly on the cart, which reduces wait times. Personalization uses data from past purchases and in-store behavior to suggest relevant products and deals. Digital advertising on cart screens delivers targeted promotions based on location and cart contents, encouraging impulse buys. Social commerce features connect carts to social media, letting customers share products and access reviews. These innovations help build loyalty and make shopping more enjoyable for every customer.
Retail Innovation
Retailers use smart technology to simplify and personalize the shopping experience. AI, IoT, sensors, and RFID technology eliminate traditional checkout lines through instant product detection and contactless payment. Real-time inventory insights and customer behavior data help optimize store layouts and promotions. Major retailers like Walmart and Amazon lead the way with robot-powered and cashierless solutions. As costs decrease, specialty and smaller stores also adopt these technologies. Companies such as Grabango, IMAGR, and Shopic provide scalable solutions that support rapid, accurate checkout and enhanced customer engagement. Smart carts reduce the need for checkout clerks, allowing staff to focus on helping customers in the aisles. Retail media advertising on cart screens creates new revenue streams, using shopper data to maximize impact. These innovations continue to transform the retail sector and improve the experience for all customers.
Shopping carts have changed from simple metal frames to smart mobile solutions that use AI and sensors. The timeline below shows key innovations:
Decade | Innovations and Impact |
|---|---|
1960s | Child seats added for families |
1970s | Plastic carts improved durability |
1980s | Swivel wheels made carts easier to use |
1990s | Cup holders and family features added |
2000s | Self-checkout and scannable carts appeared |
2010s-2020s | Smart carts with scanning and real-time tracking |
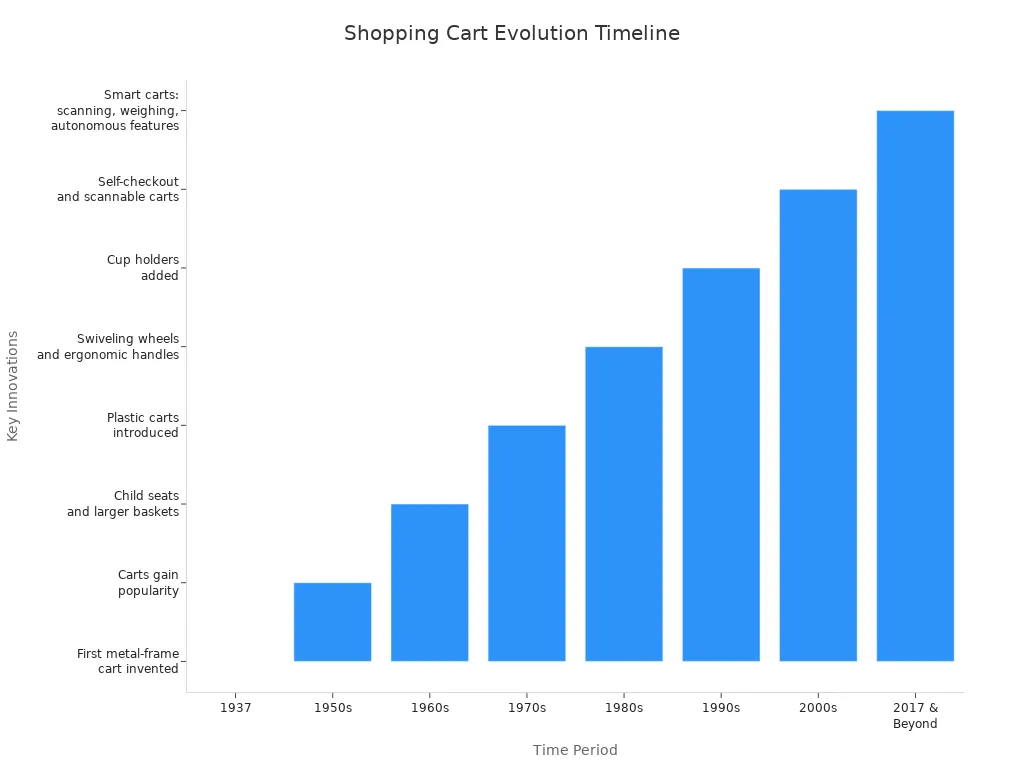
Today, smart carts help shoppers check out faster and give retailers better data. Ongoing innovation will keep making shopping easier, more personal, and more efficient for everyone.
FAQ
What is a smart shopping cart?
A smart shopping cart uses technology like sensors, cameras, and screens. It helps shoppers track items, see prices, and pay directly on the cart. These carts make shopping faster and more convenient.
How do smart carts improve the shopping experience?
Smart carts give real-time updates, show personalized offers, and speed up checkout. Shoppers can find products easily and avoid long lines. Many people enjoy the added convenience and information.
Are smart shopping carts secure?
Retailers use strong security measures to protect customer data. Smart carts often use encryption and secure payment systems. Shoppers should always check for trusted brands and privacy policies.
Can smart carts help retailers save money?
Smart carts reduce labor costs by automating checkout.
They help manage inventory with real-time data.
Stores can use shopper data to improve marketing and product placement.
See Also
Smart Technology Is Changing The Future Of Vending Machines
AI Tools Are Redefining The Way Online Stores Operate
The Rise Of Smart Stores Shaping Convenience Retail Trends
Cloudpick Enables Seamless Cashierless Shopping Experiences Today
